When your car battery dies, it can leave you in a frustrating situation – your key stuck in the ignition. However, there's a straightforward solution to this problem. This guide will walk you through the process of safely removing your key using the manual override mechanism.
Automatic Transmission Shifting Hard? Causes & Fixes for Rough Gear Changes
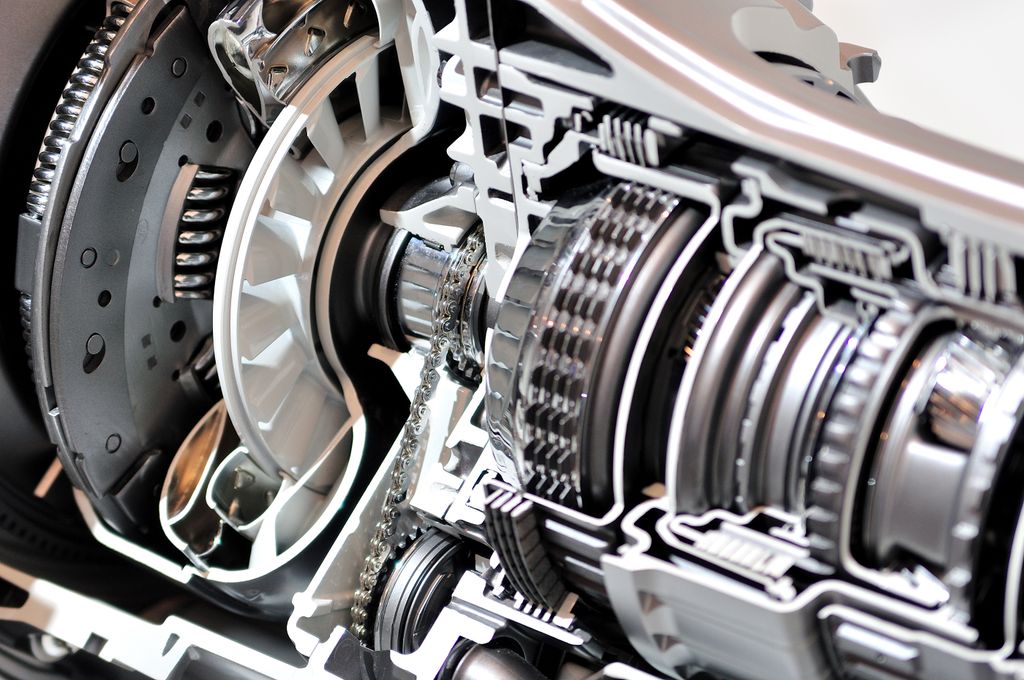
Automatic Transmission Shifting Hard? Causes & Fixes for Rough Gear Changes
Introduction
An automatic transmission is a complex system that ensures smooth gear changes as your vehicle accelerates or decelerates. When it starts shifting gears roughly or with a jerk, it can be an indication of an underlying issue that needs attention. Rough gear changes not only make for an unpleasant driving experience but can also lead to further transmission damage if left unaddressed.

Understanding the Problem
When an automatic transmission shifts gears harshly, it can feel like a sudden jolt or a rough, jerking motion. This can happen during acceleration, deceleration, or even when the vehicle is cruising at a steady speed. It's a clear indication that something isn't quite right with the transmission system.
The sensation of a harsh shift can range from a noticeable thump or clunk to a violent shudder that can be felt throughout the entire vehicle. In some cases, the shift may even cause the engine to rev up unexpectedly or the vehicle to momentarily lose power. These symptoms can be unsettling and may leave you wondering if your transmission is on the verge of failure.
Main Causes of Automatic Transmission Shifting Hard
Over the years, I've identified several common culprits that can lead to this issue. Let's dive into the main causes and explore them in detail.
Low or Contaminated Transmission Fluid
Transmission fluid plays a crucial role in lubricating and providing hydraulic pressure for smooth gear changes. When the fluid level is low or the fluid itself is contaminated or degraded, it can cause delayed or harsh shifts.
| Symptoms | Potential Causes |
|---|---|
| Delayed or harsh shifts | Low fluid level |
| Slipping or erratic shifting | Contaminated or degraded fluid |
| Transmission overheating | Fluid breakdown due to excessive heat |
Imagine the transmission fluid as the lifeblood of your transmission – without the proper amount and quality, the entire system struggles to function correctly. Low fluid levels can occur due to leaks or simply not being topped up regularly, while contamination can happen due to excessive heat, moisture, or debris entering the system.
Worn Clutch Components
Inside the transmission, there are clutches and bands that engage and disengage to facilitate gear changes. Over time, the friction material on these components can wear out, causing them to grab unevenly and shift roughly.
Clutch packs
Brake bands
Friction plates
Steel plates
Think of it like trying to change gears with worn-out clutch plates in a manual transmission – the engagement becomes erratic and unpredictable, leading to those dreaded harsh shifts.
Faulty Sensors or Solenoids
Modern automatic transmissions rely on various sensors and solenoids to control fluid flow and gear changes. If any of these components malfunction, it can result in improper shifting behavior.
Common Sensors and Solenoids:
Transmission speed sensors
Throttle position sensors
Shift solenoids
Pressure control solenoids
These sensors and solenoids act as the transmission's eyes and ears, providing vital information to the computer about speed, throttle position, and fluid pressure. When they fail, the transmission essentially becomes blind and can't make smooth, well-timed shifts.
Transmission Mounts Issues
Worn or broken transmission mounts can cause excessive movement, disrupting the precise alignment between the engine and transmission. This misalignment can lead to harsh shifts and vibrations.
| Mount Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Rear mount | Supports the transmission at the rear |
| Center mount | Secures the transmission to the engine |
| Side mounts | Stabilize the transmission laterally |
Imagine trying to shift gears while the transmission is bouncing around – it's bound to be a rough and uncomfortable experience. Proper mounting is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance and alignment required for smooth shifting.
Computer/Software Glitches
In today's vehicles, automatic transmissions are computer-controlled, and software issues or glitches can cause erratic shifting behavior or adaptation problems.
Think of the transmission computer as the brain behind the operation – if it's not functioning correctly or has outdated software, it can send the wrong signals, leading to improper gear changes and harsh shifts.
Checking and Diagnosing the Issue
As a mechanic, my first step in addressing any transmission issue is to perform a thorough inspection and diagnosis. Here's what I typically do:

Check the transmission fluid level and condition: I'll inspect the fluid level and look for any signs of contamination, such as a burnt smell, discoloration, or the presence of metal particles or debris.
Inspect for leaks: Any fluid leaks can contribute to low fluid levels and potential contamination, so I'll carefully check for any signs of leakage around the transmission case, cooler lines, and other components.
Observe warning lights: I'll check the dashboard for any warning lights related to the transmission, such as the "Check Engine" light or a dedicated transmission warning light. These can provide valuable diagnostic information and help pinpoint the issue.
Perform a test drive: Nothing beats experiencing the shifting issues firsthand, so I'll take the vehicle for a test drive to evaluate the severity and consistency of the problem. I'll pay attention to when the harsh shifts occur (e.g., during acceleration, deceleration, or cruising) and any other accompanying symptoms.
Based on my observations and diagnostic findings, I can often pinpoint the specific cause of the harsh shifting. For example, delayed engagement or slipping gears may indicate low fluid, worn clutches, or solenoid issues, while erratic or inconsistent shifting patterns could point to sensor or computer faults.
Repair Instructions for Specific Causes
Once I've identified the root cause, it's time to address the issue head-on. Here are some common repair procedures I follow for specific causes:
Fluid-related Issues
If the problem is related to low or contaminated transmission fluid, the solution is relatively straightforward. I'll drain and refill the transmission with new, recommended fluid and replace the filter. If there are any leaks, I'll repair them by replacing gaskets, seals, or lines as needed.
Worn Clutch Components
When clutch components are worn, the transmission needs to be disassembled and rebuilt. This involves replacing worn clutch packs, bands, and other internal components that have reached the end of their service life.
The process typically involves:
Removing the transmission from the vehicle
Disassembling the transmission case
Inspecting and replacing worn components
Reassembling the transmission with new parts
Reinstalling the rebuilt transmission into the vehicle
Faulty Sensors/Solenoids
In cases where sensors or solenoids are malfunctioning, I'll diagnose and replace the faulty components. Depending on the issue, this may also require reprogramming or software updates to ensure proper communication between the transmission and the control module.
The repair process may involve:
Accessing and testing individual sensors or solenoids
Replacing defective components with new ones
Updating the transmission control module software (if applicable)
Performing relearn procedures to calibrate the new components
Transmission Mounts
If the transmission mounts are worn or broken, I'll replace them with new ones and ensure proper alignment and secure mounting. This helps eliminate any excessive movement that could contribute to harsh shifts.
The steps typically include:
Supporting the transmission with a transmission jack
Removing the old mounts
Installing new mounts and tightening them to the specified torque
Checking for proper alignment and clearance
Computer Issues
For computer or software-related issues, I'll perform diagnostic scans and clear any trouble codes. If available, I'll update the transmission control module software to the latest version. In some cases, a complete transmission rebuild may be necessary to address underlying hardware issues.
The repair process may involve:
Connecting a diagnostic scan tool to the vehicle's computer system
Reading and clearing any transmission-related trouble codes
Updating the transmission control module software (if available)
Performing any necessary relearn or adaptation procedures
Throughout the repair process, I always follow the manufacturer's recommended procedures and specifications, using high-quality transmission fluids and genuine replacement parts. Complex repairs or transmission rebuilds may require the assistance of specialized transmission shops or technicians.
Preventing Recurrence
While repairs can address the immediate issue, it's equally important to take preventive measures to avoid future transmission problems. Here are some tips I recommend:
Regular Maintenance
Adhering to the recommended maintenance schedule is crucial. This includes changing the transmission fluid and filter at the specified intervals, as well as inspecting for any leaks or worn components during routine services.
| Maintenance Task | Recommended Interval |
|---|---|
| Transmission fluid and filter change | Every 30,000 - 60,000 miles (or as specified by the manufacturer) |
| Inspection for leaks and wear | During regular service intervals |
Proper Usage and Operation
Aggressive driving habits, such as hard acceleration or excessive engine braking, can put unnecessary strain on the transmission. It's best to avoid these practices and allow the transmission to warm up before putting it under load. Additionally, never exceed the vehicle's towing or payload capacity, as this can also contribute to premature wear and tear.
| Driving Practice | Impact on Transmission |
|---|---|
| Hard acceleration | Increased stress on clutches and bands |
| Excessive engine braking | Excessive heat buildup and wear |
| Overloading the vehicle | Increased strain on components |
Cost Considerations
The cost of repairing an automatic transmission can vary significantly depending on the specific issue and the extent of the damage. Here are some general estimates:
Fluid change and filter replacement: $100 - $300
Sensor or solenoid replacement: $200 - $800
Transmission mount replacement: $200 - $500
Transmission rebuild or overhaul: $1,500 - $4,000
Complete transmission replacement: $2,500 - $7,000 (depending on the vehicle)
It's important to note that these costs can vary based on factors such as the make and model of the vehicle, labor rates in your area, and the availability of parts. Additionally, some repairs may be covered under the vehicle's warranty or an extended warranty plan. Seeking multiple quotes from reputable transmission repair shops is recommended to find the best price and service.
Conclusion
Dealing with an automatic transmission that shifts hard can be a frustrating experience, but with the right knowledge and approach, it's a problem that can be resolved. As a mechanic, I've seen firsthand how proper maintenance, diagnosis, and repair can restore smooth shifting and extend the life of your transmission.
Remember, addressing transmission issues promptly is crucial to prevent further damage and costly repairs down the line. If you ever experience harsh shifting or any other transmission-related concerns, don't hesitate to seek professional assistance. A skilled mechanic can diagnose the issue accurately and provide the appropriate solution to get you back on the road with a smooth-shifting transmission.
FAQs
What causes automatic transmission to shift hard from 1st to 2nd gear?
Low or contaminated transmission fluid and worn clutch components are common culprits for hard shifts between 1st and 2nd gear. Faulty sensors or solenoids can also contribute to this issue.
How do I know if my transmission fluid needs to be changed?
Check your owner's manual for the recommended fluid change interval. Also, inspect the fluid color and smell - discolored or burnt-smelling fluid indicates it needs replacement.
Can a clogged transmission filter lead to hard shifting?
Yes, a clogged transmission filter can restrict fluid flow, causing a drop in hydraulic pressure and resulting in harsh gear shifts.
What role do transmission mounts play in shifting quality?
Worn or broken transmission mounts can cause excessive movement and misalignment between the engine and transmission, leading to harsh shifts and vibrations.
How do I check for transmission sensor issues?
A mechanic with proper diagnostic equipment can check the sensors and look for any trouble codes related to faulty speed sensors, throttle position sensors, etc.
Is it safe to drive with a transmission that shifts hard occasionally?
It's generally not recommended to continue driving if the transmission exhibits frequent hard shifting, as it can lead to further internal damage.
Can aggressive driving habits cause hard shifting over time?
Yes, habits like rapid acceleration and engine braking can put extra strain on the transmission components, potentially resulting in premature wear and harsh shifting.
What are the cost estimates for common transmission repairs?
Costs can vary, but a fluid change may cost $100-$300, while more major repairs like a solenoid replacement ($200-$800) or a complete rebuild ($1,500-$4,000) can be expensive.
How often should I get my transmission serviced?
Follow your vehicle's recommended maintenance schedule, which typically advises transmission fluid and filter changes every 30,000 to 60,000 miles.
Can software issues cause erratic shifting in modern transmissions?
Yes, computer-controlled transmissions can experience software glitches or adaptation problems that lead to erratic shifting behavior, sometimes requiring a software update or relearn procedure.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
Coolant, also known as antifreeze, plays a vital role in your vehicle's cooling system, preventing engine overheating and freeze-up. However, like any other automotive fluid, coolant has a limited lifespan and requires regular maintenance and replacement. In this article, we'll explore the factors that affect coolant shelf life, signs of degradation, and best practices for ensuring optimal cooling system performance.
Brakes are essential components of any vehicle, ensuring the safety of passengers and other road users. Understanding the different types of brakes and their functions is crucial for making informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and upgrades. In this article, we will explore the various brake systems found in modern vehicles, including disc brakes, drum brakes, hydraulic brakes, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and regenerative brakes. We will also discuss brake maintenance, high-performance upgrades, and future trends in brake technology.
An engine flush is a maintenance procedure that involves introducing a chemical solution into the engine to remove accumulated sludge, deposits, and contaminants.
Bài viết liên quan
A car's transmission is a complex system responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move and change gears smoothly. When a transmission starts slipping gears, it can be a sign of an underlying issue that needs to be addressed promptly.
Transmission fluid is a specialized lubricant designed to meet the unique demands of a vehicle's transmission. It serves several vital purposes
A humming noise coming from the transmission while accelerating is a common issue that many car owners face. This noise can be an indication of various underlying problems within the transmission system, ranging from minor issues to more severe ones that require immediate attention.
Braking is a critical skill for safe driving, yet many drivers struggle to bring their vehicles to a smooth and controlled stop. Abrupt or jerky braking can lead to discomfort for passengers, potential loss of control, and increased wear on the vehicle's components.
The clutch is a crucial component in vehicles with manual transmissions, enabling smooth gear changes and power transfer from the engine to the wheels. Over time, the clutch can wear out due to normal usage, improper driving techniques, or other factors.
A transmission leak can be a serious issue that, if left unaddressed, can lead to costly repairs or even complete transmission failure. The transmission is a vital component of your vehicle, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing you to shift gears smoothly.
Automatic transmissions have become an integral part of modern vehicles, revolutionizing the driving experience and offering convenience and efficiency. These sophisticated systems have evolved significantly since their inception, incorporating advanced technologies and innovative designs to meet the ever-increasing demands of the automotive industry.
A clutch is a crucial component in a manual transmission vehicle that allows the engine to be temporarily disconnected from the transmission, enabling smooth gear changes. When the clutch is fully engaged, it transfers the engine's power to the transmission, propelling the vehicle forward.
The transmission is a critical component in a vehicle's drivetrain. It plays a crucial role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to operate at different speeds and under varying driving conditions.













