Towing capacity is a critical factor to consider when purchasing a vehicle intended for hauling trailers, boats, or other heavy loads. The Kia Sorento, a popular mid-size SUV, stands out with its remarkable towing capabilities, making it a versatile choice for families and outdoor enthusiasts alike.
Carb Cleaner vs Brake Cleaner: Unraveling the Crucial Differences
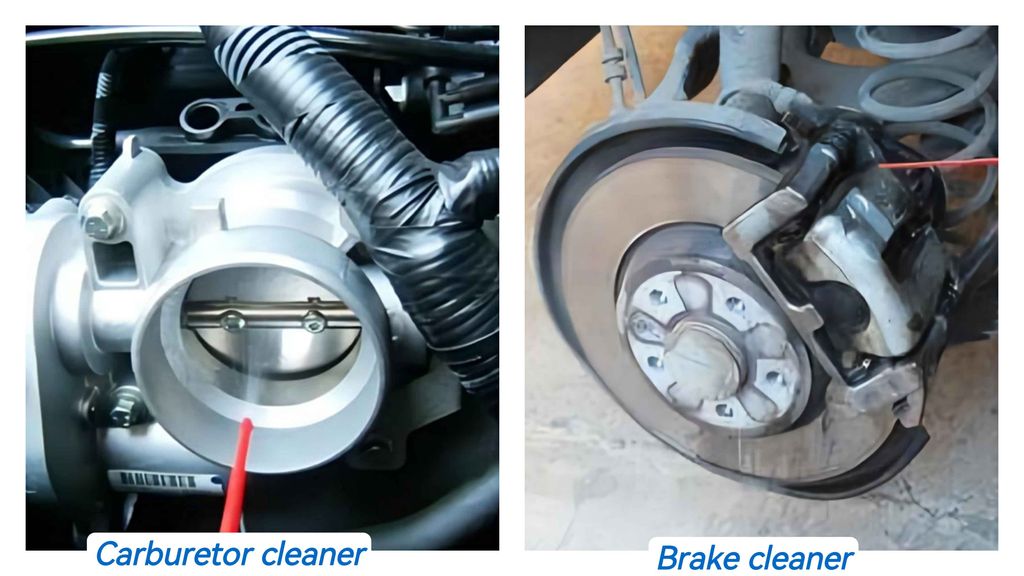
Carb Cleaner vs Brake Cleaner: Unraveling the Crucial Differences
Automotive maintenance is a complex task that requires a deep understanding of various components and the specialized products designed to keep them in optimal condition. Among these products, carb cleaners and brake cleaners play a vital role, yet their distinct compositions, intended uses, and safety considerations often lead to confusion and interchangeable usage, which can potentially compromise the effectiveness of the cleaning process or even cause damage. This comprehensive article aims to unravel the crucial differences between these two essential automotive cleaning products, shedding light on their compositions, intended uses, safety precautions, material compatibility, additional applications, and cost and availability.

Introduction
Automotive maintenance encompasses a wide range of tasks, from routine inspections to specialized cleaning procedures. Proper cleaning of fuel system components and brake assemblies is crucial for ensuring efficient operation and prolonged service life. Carb cleaners and brake cleaners are specifically formulated to address these distinct cleaning needs, making it essential to understand their unique characteristics and applications.
| Product | Carb Cleaner | Brake Cleaner |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Acetone, Toluene, Methanol, Carbon Dioxide (propellant) | Acetone, Heptane, Toluene, Carbon Dioxide (propellant) |
| Key Difference | Contains Methanol | Lacks Methanol |
Composition and Ingredients
Carb cleaners are formulated with a potent blend of solvents, including acetone, toluene, and methanol, designed to effectively dissolve and remove stubborn deposits and contaminants from fuel system components. These cleaners also contain carbon dioxide as a propellant, which aids in the delivery and penetration of the cleaning solution.
Brake cleaners, on the other hand, are composed of a different solvent mixture, typically consisting of acetone, heptane, and toluene. Notably, they lack methanol, a key ingredient found in carb cleaners. Like carb cleaners, brake cleaners also utilize carbon dioxide as a propellant to facilitate the cleaning process.
The absence of methanol in brake cleaners is a crucial distinction, as methanol can potentially damage or degrade certain materials commonly found in brake systems, such as rubber and plastic components.
Intended Uses
Carb cleaners are specifically designed for cleaning carburetors, fuel injectors, throttle bodies, and other components of the fuel delivery system. Their potent solvent formulation effectively removes varnish, gum, and other deposits that can accumulate over time, impeding the proper functioning of these critical components.
| Carb Cleaner Intended Uses |
|---|
| Cleaning carburetors |
| Cleaning fuel injectors |
| Cleaning throttle bodies |
| Removing varnish deposits |
| Removing gum deposits |
In contrast, brake cleaners are intended for cleaning brake components, including discs, pads, calipers, and drums. These cleaners are formulated to remove brake fluid, grease, oil, and brake dust that can accumulate on these components, potentially compromising braking performance and safety.
| Brake Cleaner Intended Uses |
|---|
| Cleaning brake discs |
| Cleaning brake pads |
| Cleaning brake calipers |
| Cleaning brake drums |
| Removing brake fluid |
| Removing grease |
| Removing oil |
| Removing brake dust |
Using the wrong cleaner for a particular application can lead to ineffective cleaning or even damage to components, highlighting the importance of understanding and adhering to the intended uses of each product.
Safety Precautions
Both carb cleaners and brake cleaners are considered hazardous materials due to their flammable nature and the presence of potent solvents. As such, proper safety precautions are essential when using these products.
Working in a well-ventilated area is crucial to prevent the accumulation of potentially harmful vapors. Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and eye protection, is highly recommended to minimize exposure to these hazardous materials.
| Safety Precautions |
|---|
| Well-ventilated area |
| Wear gloves |
| Wear eye protection |
| Avoid open flames |
| Avoid sparks |
Material Compatibility
Carb cleaners are generally safe for use on rubber and plastic components commonly found in fuel systems, as they are formulated to be compatible with these materials. However, brake cleaners can potentially damage or degrade rubber, plastic, and painted surfaces. Therefore, it is crucial to use brake cleaners only on metal components to avoid any unintended damage.
| Material Compatibility | Carb Cleaner | Brake Cleaner |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber Components | Safe | Can Damage |
| Plastic Components | Safe | Can Damage |
| Painted Surfaces | Safe | Can Damage |
| Metal Components | Safe | Safe |
Failure to consider material compatibility can lead to premature wear, degradation, or even component failure, underscoring the importance of following manufacturer guidelines and exercising caution when using these cleaning products.
Additional Uses

While carb cleaners and brake cleaners are designed for their respective primary purposes, their potent solvent properties make them versatile for additional applications.
Carb cleaners can be used to remove stubborn stains or grease from various surfaces, as well as for degreasing tools or other equipment. Their ability to dissolve and remove stubborn deposits makes them effective for a wide range of cleaning tasks.
Similarly, brake cleaners can be utilized for degreasing metal components and tools, in addition to their primary function of cleaning brake assemblies. Their ability to effectively remove grease, oil, and other contaminants from metal surfaces makes them versatile cleaning agents in automotive workshops and garages.
| Additional Uses | Carb Cleaner | Brake Cleaner |
|---|---|---|
| Removing stains | Yes | No |
| Degreasing tools | Yes | Yes |
| Cleaning metal components | No | Yes |
Cost and Availability
Carb cleaners are generally less expensive than brake cleaners, making them a cost-effective choice for routine maintenance and cleaning tasks. These products are widely available at automotive stores, hardware stores, and online retailers, ensuring easy accessibility for consumers and professionals alike.
In contrast, brake cleaners tend to be more expensive due to their specialized formulation and intended use. However, they are readily available at hardware stores, automotive stores, and online retailers, ensuring that consumers and professionals can easily obtain these products when needed.
| Availability | Carb Cleaner | Brake Cleaner |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Stores | Yes | Yes |
| Hardware Stores | Yes | Yes |
| Online Retailers | Yes | Yes |
Conclusion
In the intricate world of automotive maintenance, understanding the distinctions between carb cleaners and brake cleaners is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle's components. By recognizing their unique compositions, intended uses, safety considerations, and material compatibility, you can make informed decisions and employ the appropriate cleaning product for the task at hand.
Remember, using the wrong cleaner can lead to ineffective cleaning or even damage to components, potentially compromising the safety and efficiency of your vehicle. Therefore, it is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines, exercise caution, and prioritize safety when working with these specialized cleaning products.
By adhering to the best practices outlined in this comprehensive article, you can confidently tackle automotive cleaning tasks, ensuring that your vehicle's fuel system and brake components remain in top condition for years to come.
FAQs
What is the difference between carb cleaner and brake cleaner?
Carb cleaner contains methanol which helps protect rubber components, while brake cleaner lacks methanol to avoid damaging rubber parts in brake systems. Carb cleaner leaves behind a thin film to prevent buildup, whereas brake cleaner evaporates completely.
Can I use brake cleaner on carburetors?
No, you should not use brake cleaner on carburetors as it can potentially damage the rubber components due to the lack of methanol.
Is it safe to use carb cleaner on painted surfaces?
Yes, carb cleaner is generally safe for use on painted surfaces as it is formulated to be compatible with these materials.
What are the safety precautions when using these cleaners?
Work in a well-ventilated area, wear gloves and eye protection, and avoid open flames or sparks as these cleaners are flammable.
Can I use carb cleaner as a degreaser?
Yes, the potent solvent properties of carb cleaner make it effective for degreasing tools, equipment, and other surfaces beyond its primary use.
What is the primary intended use of brake cleaner?
Brake cleaner is specifically designed for cleaning brake components like discs, pads, calipers, and drums to remove contaminants that can affect braking performance.
How do I properly clean brake discs and pads?
Spray brake cleaner directly on the surface, let it work, then use a brush or cloth to agitate and remove the dissolved dirt and grime.
Are there any compatibility issues with brake cleaner?
Brake cleaner can potentially damage or degrade rubber, plastic, and painted surfaces, so it should only be used on metal brake components.
What makes carb cleaner more expensive than brake cleaner?
Carb cleaner is generally less expensive than brake cleaner due to its specialized formulation and intended use for brake systems.
Can I use carb cleaner as a starter fluid?
No, carb cleaner should not be used as a substitute for starter fluid as excessive amounts can cause backfiring or even engine fires.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
The Tow/Haul mode is a valuable feature found in modern vehicles equipped with automatic transmissions. It is designed to optimize the vehicle's performance and reduce strain on various components when towing or hauling heavy loads.
Douglas Tires, a brand owned and manufactured by the renowned Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company, has emerged as a popular choice for drivers seeking affordable yet reliable tires.
The Tesla Cybertruck has captured the imagination of automotive enthusiasts and electric vehicle advocates alike, promising a unique combination of rugged utility and cutting-edge technology
Bài viết liên quan
For automotive enthusiasts and DIY mechanics, maintaining a vehicle's brake system is crucial for ensuring safe and reliable performance. However, traditional brake cleaners often contain harsh chemicals that can harm the environment and pose potential health risks.





