A blend door actuator is a small electric motor that controls the temperature and airflow in a vehicle's heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system. It operates the blend door, which is a flap or door that regulates the mixture of hot and cold air from the heater core and evaporator. The number of blend door actuators in a car can vary depending on the vehicle's make, model, and HVAC system design
How To Bypass Voltage Regulator On An Alternator?
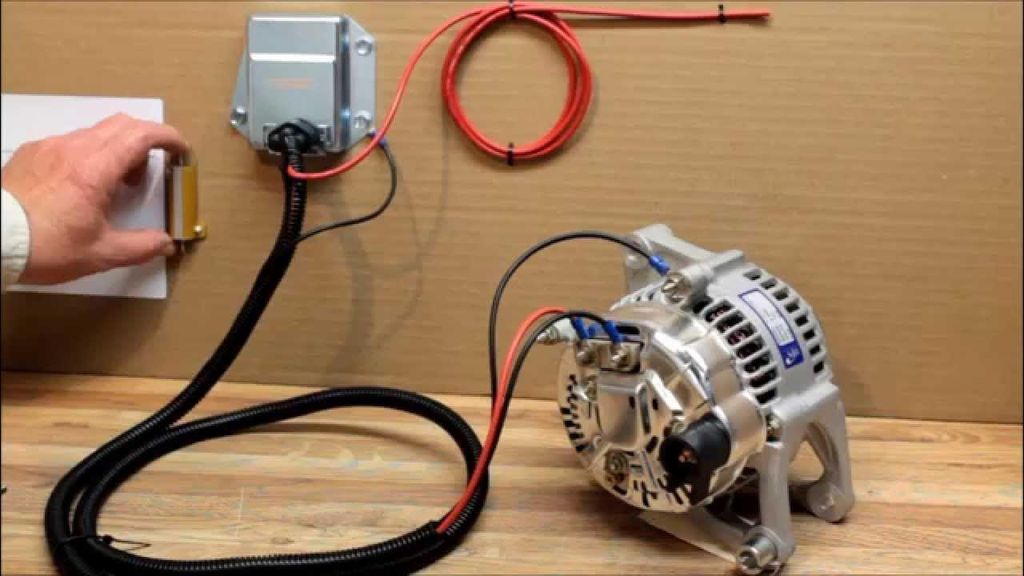
How To Bypass Voltage Regulator On An Alternator?
The alternator plays a crucial role in a vehicle's electrical system by charging the battery and powering various components. However, issues with the voltage regulator, which controls the alternator's output, can lead to charging problems. In such cases, bypassing the voltage regulator can serve as a temporary solution to diagnose and troubleshoot the issue.
This guide will walk you through the process of bypassing the voltage regulator, covering the necessary preparations, safety precautions, locating the regulator, the bypass procedure, testing the alternator's output, and understanding the associated risks. Additionally, we'll discuss the importance of proper voltage regulation and when to seek professional assistance.

Introduction
The alternator charging system consists of several components, including the alternator, voltage regulator, battery, and associated wiring. The alternator generates alternating current (AC), which is then converted to direct current (DC) to charge the battery and power the vehicle's electrical components. Voltage regulation is crucial for maintaining the proper charging voltage and preventing overcharging or undercharging of the battery.
Preparing to Bypass
Before attempting to bypass the voltage regulator, ensure you have the necessary tools and materials, and take appropriate safety precautions.
Required Tools and Materials
| Tool/Material | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Jumper wire | Connect the alternator's field terminal to the battery positive terminal |
| Voltmeter | Monitor the battery voltage and confirm proper charging |
| Basic hand tools | Access the voltage regulator and disconnect the wiring harness connector |
Safety Precautions
| Precaution | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Disconnect negative battery cable | Prevent short circuits and potential electrical shocks |
| Avoid shorts and sparks | Prevent fires or damage to the electrical system |
| Wear eye protection | Shield your eyes from potential debris or sparks |
Locating the Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator can be found in different locations depending on the vehicle make and model. Common locations include:
Rear alternator housing
Wiring harness connector
Once located, identify the specific terminals for the bypass procedure:
Field (F) terminal: Connection point for the alternator's field winding
Battery positive (B+) terminal: Connection point for the positive battery cable or alternator output wire
Bypassing the Regulator
Disconnect the wiring harness connector from the voltage regulator.
Using the jumper wire, connect the field (F) terminal on the voltage regulator connector to the battery positive (B+) terminal.
Reconnect the negative battery cable.
Testing Alternator Output
After bypassing the voltage regulator, test the alternator's output to determine if the issue lies with the regulator or the alternator itself.
Start the engine and allow it to idle.
Monitor the battery voltage using the voltmeter. A properly charging alternator should produce a voltage reading between 14 and 15 volts.
If the alternator is charging the battery correctly (14-15V) when bypassed, the voltage regulator is likely faulty and needs to be replaced. If the alternator is still not charging the battery, the issue likely lies with the alternator itself or the associated wiring, and further diagnostics or repairs may be necessary.
Risks of Running Bypassed
Running the alternator with a bypassed voltage regulator for an extended period can lead to several risks:
Overcharging the battery, potentially causing premature battery failure or damage
Damaging sensitive electrical components due to excessive voltage
Excessive heat buildup, potentially leading to premature alternator failure
Due to these risks, it's strongly recommended to bypass the voltage regulator only for diagnostic purposes and replace the faulty regulator as soon as possible.
Replacing Failed Regulator
If the bypass procedure confirms a faulty voltage regulator, follow these steps to replace it:
Obtain a replacement voltage regulator that matches the specifications of your vehicle's alternator.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions or a repair manual to properly remove the old voltage regulator and install the new one.
Reconnect the wiring harness connector and any other associated wiring, ensuring secure connections and proper routing.
Conclusion
Bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator is a useful diagnostic technique when troubleshooting charging system issues. However, it's crucial to understand the importance of proper voltage regulation and the risks associated with running a bypassed system for extended periods. If you encounter any difficulties or uncertainties, seek professional assistance to ensure the safety and longevity of your vehicle's electrical system.
FAQs
What is the purpose of bypassing the voltage regulator?
Bypassing the voltage regulator is a temporary solution to diagnose and troubleshoot charging system issues. It allows you to determine if the voltage regulator or the alternator itself is causing the problem.
What are the risks of running with a bypassed voltage regulator?
Running the alternator with a bypassed voltage regulator for an extended period can overcharge the battery, damage sensitive electrical components due to excessive voltage, and cause excessive heat buildup, potentially leading to premature alternator failure.
How do you locate the voltage regulator?
The voltage regulator is commonly found on the rear alternator housing or the wiring harness connector. Identify the specific terminals for the field (F) and battery positive (B+) connections.
What tools are required to bypass the voltage regulator?
The required tools include a jumper wire, a voltmeter to monitor the battery voltage, and basic hand tools to access the voltage regulator and disconnect the wiring harness connector.
What safety precautions should be taken before bypassing the voltage regulator?
Safety precautions include disconnecting the negative battery cable, avoiding shorts and sparks, and wearing eye protection to shield your eyes from potential debris or sparks.
How do you test the alternator output after bypassing the voltage regulator?
After bypassing the voltage regulator, start the engine and monitor the battery voltage using a voltmeter. A properly charging alternator should produce a voltage reading between 14 and 15 volts.
What should you do if the alternator charges correctly when bypassed?
If the alternator charges correctly (14-15V) when bypassed, the voltage regulator is likely faulty and needs to be replaced.
What should you do if the alternator does not charge correctly when bypassed?
If the alternator is still not charging the battery, the issue likely lies with the alternator itself or the associated wiring, and further diagnostics or repairs may be necessary.
How do you replace a failed voltage regulator?
To replace a failed voltage regulator, obtain a replacement that matches your vehicle's alternator specifications, follow the manufacturer's instructions or a repair manual to remove the old regulator and install the new one, and reconnect the wiring harness and associated wiring securely.
Why is it important to replace a faulty voltage regulator?
It is important to replace a faulty voltage regulator as soon as possible to prevent overcharging the battery, damaging sensitive electrical components, and causing excessive heat buildup, which can lead to premature alternator failure.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
The oil pressure gauge is an essential instrument in a vehicle's engine that monitors the oil pressure within the lubrication system. It provides crucial information about the engine's health and alerts the driver to potential issues.
As an experienced automotive mechanic, I've encountered countless car owners who have asked me the same question: "Why does my car rev in park?" It's a common issue that can be both perplexing and concerning for drivers.
Greetings, fellow automotive enthusiasts! Buckle up as we delve into the intricate world of diagnostic codes, specifically the notorious P0390. As a seasoned mechanic with years of experience under my belt, I've encountered this code countless times, and each encounter has been a unique learning experience. Today, I'm thrilled to share my insights and provide you with a comprehensive guide to understanding and tackling this perplexing code.



