A humming noise coming from the transmission while accelerating is a common issue that many car owners face. This noise can be an indication of various underlying problems within the transmission system, ranging from minor issues to more severe ones that require immediate attention.
Are CVT Transmissions Reliable? The Truth About Continuously Variable Transmissions
Are CVT Transmissions Reliable? The Truth About Continuously Variable Transmissions
Introduction
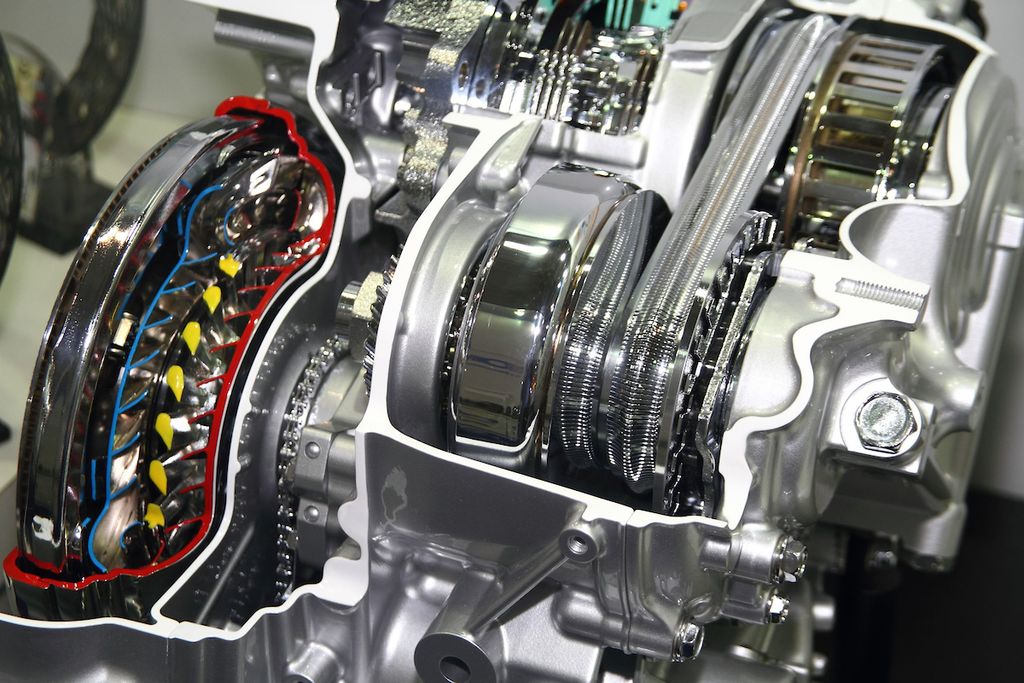
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) are a type of automatic transmission that have gained popularity in recent years due to their potential for improved fuel efficiency and smoother operation compared to traditional automatic transmissions. Unlike conventional automatic transmissions that use a fixed set of gears, CVTs work by using a system of pulleys and a metal belt or chain to provide an infinite number of gear ratios.

Understanding CVT Transmissions
Before we dive into the reliability aspect, let's take a moment to understand what a CVT transmission is and how it works. Unlike traditional automatic transmissions with fixed gear ratios, CVTs employ a unique design that utilizes a pair of pulleys connected by a steel belt or chain. As the pulleys adjust their diameters, the effective gear ratio changes seamlessly, providing an infinite range of gear ratios. This innovative design allows for smoother acceleration, improved fuel efficiency, and a more responsive driving experience.
Main Causes of CVT Transmission Issues
While CVTs offer several advantages, they are not immune to potential problems. Throughout my professional experience, I've encountered various issues that can arise with CVT transmissions. Here are some of the main causes:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Overheating | CVTs operate at higher temperatures compared to traditional transmissions, and excessive heat can damage the pulleys, belt, and other internal components, leading to premature wear and potential failure. Overheating can be caused by factors such as towing heavy loads, frequent stop-and-go driving, or a malfunctioning cooling system. |
| Fluid Leakage and Contamination | Like any other transmission, CVTs rely on transmission fluid to lubricate and cool the internal components. Low fluid levels or contaminated fluid can cause excessive wear, slippage, and ultimately, transmission failure. Fluid leaks can occur due to worn seals, gaskets, or other components, while contamination can result from neglecting regular fluid changes or using the wrong type of fluid. |
| Mechanical Wear | Over time, the belt, pulleys, bearings, and other moving parts within the CVT can experience wear and tear. This mechanical wear can lead to slippage, shuddering, and eventual transmission failure if not addressed promptly. Factors like driving habits, mileage, and proper maintenance can influence the rate of wear on these components. |
Checking and Identifying CVT Transmission Issues
As a mechanic, I follow a systematic approach to diagnose CVT transmission issues. Here are the steps I typically take:
Inspection Steps
Check transmission fluid level and condition (color, smell)
Listen for unusual noises (whining, grinding, etc.)
Observe for slippage, delayed acceleration, or jerking during acceleration
Check for leaks around the transmission
Scan for diagnostic trouble codes
Signs of Specific Issues
| Issue | Signs |
|---|---|
| Overheating | Burning smell, slippage, transmission warning lights |
| Fluid Leakage | Low fluid level, puddles under the vehicle, staining around the transmission |
| Mechanical Wear | Slippage, shuddering, unusual noises |
Repairing Specific CVT Transmission Issues
Once the issue has been identified, the appropriate repair procedure can be undertaken. Here are some common repair approaches for CVT transmissions:
Overheating Repair
Replace the transmission fluid and filter
Inspect and replace the cooler lines if necessary
Check for proper operation of the cooling system (radiator, fans, etc.)
Fluid Leakage Repair
Locate and repair the leak source (seals, gaskets, etc.)
Replace the transmission fluid and filter
Mechanical Wear Repair
Disassemble the transmission and inspect for worn components
Replace the belt, pulleys, bearings, or other worn parts as needed
Reassemble and refill with fresh transmission fluid
General Repair Tips
Follow the manufacturer's repair procedures and specifications
Use only the recommended transmission fluid for your vehicle
Ensure proper alignment and adjustment of components during reassembly
Preventing Recurring CVT Transmission Issues
While repairs can address immediate issues, preventive maintenance is key to ensuring the long-term reliability of your CVT transmission. Here are some tips to help prevent recurring problems:

Regular Maintenance
Follow the manufacturer's recommended service intervals for fluid changes and inspections
Use only the specified transmission fluid for your vehicle
Proper Usage and Operation
Avoid excessive idling or high-load operation, which can cause overheating
Don't tow heavy loads or operate the vehicle outside its intended use
Warm up the transmission before driving, especially in cold weather
Cost of CVT Transmission Repair
The cost of CVT transmission repair can vary widely depending on the extent of the damage and the specific repair required. Here are some general cost estimates:
| Repair Type | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Fluid Change | $100 - $300 |
| Minor Repairs (seals, gaskets) | $300 - $800 |
| Major Repairs (belt, pulleys, bearings) | $1,500 - $3,500 |
| Complete Transmission Replacement | $3,000 - $7,000 (including labor) |
It's important to note that these costs are approximate and can vary based on your location, vehicle make and model, and the repair shop's labor rates. It's always recommended to get a detailed estimate from a reputable transmission repair shop before proceeding with any major repairs.
Conclusion
In my professional experience, CVT transmissions can be reliable when properly maintained and operated within their intended design parameters. However, like any mechanical system, they are susceptible to wear and potential issues, particularly if neglected or subjected to excessive strain.
By following the recommended maintenance schedules, using the correct transmission fluid, and avoiding excessive loads or high-temperature operation, you can help extend the lifespan of your CVT transmission. Additionally, addressing any issues promptly and seeking professional assistance from qualified mechanics can prevent minor problems from escalating into more costly repairs.
While the cost of CVT transmission repair can be substantial, it's often more economical than a complete replacement, especially for newer vehicles. By being proactive with maintenance and attentive to any warning signs, you can maximize the reliability and longevity of your vehicle's CVT transmission.
FAQs
What is the key difference between CVT and traditional automatic transmissions?
CVTs use a pulley system with a steel belt/chain to provide an infinite range of gear ratios, while traditional automatics have a fixed set of gear ratios. This allows for smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency in CVTs.
What causes overheating issues in CVT transmissions?
CVTs operate at higher temperatures, and overheating can be caused by factors like towing heavy loads, frequent stop-and-go driving, or a malfunctioning cooling system.
How can fluid leakage and contamination affect a CVT transmission?
Low fluid levels or contaminated fluid can cause excessive wear, slippage, and ultimately, transmission failure in CVTs.
What are the signs of mechanical wear in a CVT transmission?
Signs of mechanical wear include slippage, shuddering, and unusual noises from the transmission.
What is the typical repair approach for overheating issues in CVTs?
The repair approach involves replacing the transmission fluid and filter, inspecting and replacing cooler lines if necessary, and ensuring proper operation of the cooling system.
How can regular maintenance help prevent recurring CVT transmission issues?
Following the manufacturer's recommended service intervals for fluid changes and inspections, and using the specified transmission fluid, can help prevent recurring issues.
What is the cost range for a complete CVT transmission replacement?
A complete CVT transmission replacement can cost between $3,000 and $7,000, including labor.
Can driving habits affect the lifespan of a CVT transmission?
Yes, avoiding excessive idling, high-load operation, and towing heavy loads can help extend the lifespan of a CVT transmission.
What should be done if warning signs of CVT transmission issues are noticed?
If warning signs like slippage, shuddering, or unusual noises are noticed, it's recommended to address the issues promptly and seek professional assistance from qualified mechanics.
Is it possible to extend the lifespan of a CVT transmission through proper maintenance?
Yes, by following the recommended maintenance schedules, using the correct transmission fluid, and avoiding excessive strain, it is possible to extend the lifespan of a CVT transmission.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
Brake pads are essential components that enable a vehicle to decelerate and stop safely. They are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and provide consistent braking performance throughout their lifespan.
Brake pads are a critical component of a vehicle's braking system, responsible for creating the necessary friction to slow down and stop the vehicle. Their importance in ensuring safety cannot be overstated, as they play a crucial role in preventing accidents and protecting the lives of drivers, passengers, and pedestrians.
The 2.7L EcoBoost engine, introduced by Ford in 2015, has gained popularity for its impressive power and fuel efficiency. However, this turbocharged and direct-injected gasoline engine has also been subject to several common issues that prospective buyers and current owners should be aware of
Bài viết liên quan
The amount of transmission fluid required for your vehicle depends on several factors, including the make, model, year, and transmission type. Transmission fluid plays a crucial role in lubricating and cooling the transmission components, ensuring smooth gear shifts and efficient power transfer from the engine to the wheels. Maintaining the proper fluid level is essential for the longevity and performance of your transmission.
Transmission fluid is a vital component in a vehicle's transmission system, acting as a lubricant and hydraulic fluid. It helps ensure smooth gear shifts, prevents excessive wear and tear on the transmission components, and aids in cooling the transmission.
Automatic transmissions are widely used in modern vehicles due to their convenience and ease of operation. Unlike manual transmissions that require a clutch pedal to disengage the engine from the transmission during gear shifts, automatic transmissions rely on a crucial component called the torque converter to facilitate smooth power transfer and prevent engine stalling.
Transmission fluid is a vital component in the proper functioning of a vehicle's transmission system. It serves as a lubricant and coolant, ensuring smooth operation and preventing excessive wear and tear on the transmission components
Changing transmission fluid is an important maintenance task for vehicles, as the fluid plays a crucial role in lubricating and cooling the transmission components. Over time, the fluid can break down and become contaminated, leading to potential transmission issues.









