When your Honda Odyssey refuses to start, it can be a frustrating and inconvenient situation. However, by understanding the potential causes and following a systematic approach, you can often identify and resolve the issue effectively. This article will guide you through the most common reasons why your Odyssey may not start and provide practical solutions to get you back on the road.
Axle Bearing vs Wheel Bearing: Understanding the Crucial Difference
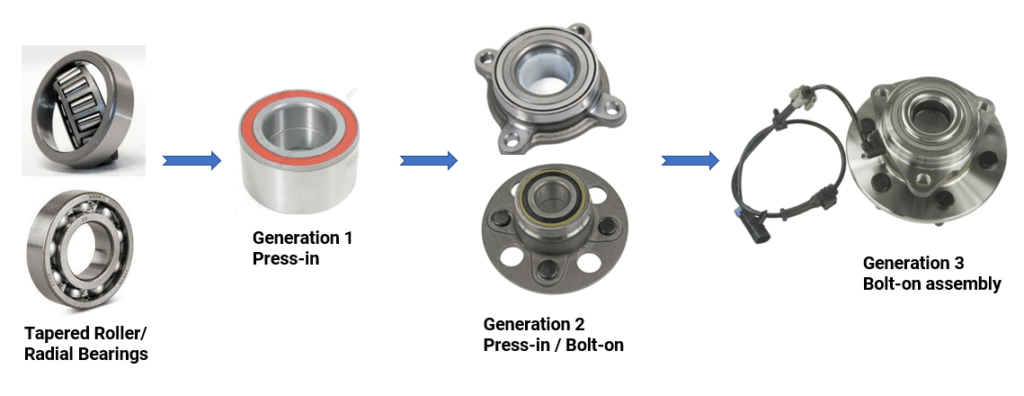
Axle Bearing vs Wheel Bearing: Understanding the Crucial Difference
Ensuring a smooth and safe driving experience requires a comprehensive understanding of the critical components that make up a vehicle's drivetrain and suspension system. Among these components, axle bearings and wheel bearings play vital roles, yet there is often confusion between the two. This article aims to clarify the distinction between axle bearings and wheel bearings, their functions, and their importance in maintaining vehicle performance and safety.

Introduction
| Component | Axle Bearing | Wheel Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Location | End of axle shafts | Inside wheel hub assembly |
| Primary Function | Support vehicle weight and allow axle rotation | Enable smooth wheel rotation and reduce friction |
Axle bearings and wheel bearings are essential components that contribute to the overall operation and longevity of a vehicle. While they serve different purposes, both play crucial roles in facilitating efficient rotation, supporting loads, and ensuring a smooth and controlled driving experience.
Types and Applications
Axle bearings and wheel bearings come in various types, each designed to handle specific load and operating conditions. Understanding these types is essential for selecting the appropriate bearings for a particular vehicle and application.
Axle Bearing Types
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Bearings | Small spherical balls roll between inner and outer rings | Front-wheel-drive vehicles, handling radial loads |
| Roller Bearings | Cylindrical rollers instead of balls | Various applications, handling radial and axial loads |
| Tapered Roller Bearings | Tapered rollers angled to accommodate radial and axial loads | Heavy-duty applications, trucks, and trailers |
Wheel Bearing Types
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Bearings | Small spherical balls roll between inner and outer rings | Passenger vehicles, lighter-duty applications, handling radial loads |
| Tapered Roller Bearings | Tapered rollers angled to accommodate radial and axial loads | Heavier vehicles, high-load applications |
Critical Functions and Importance
Axle bearings and wheel bearings play distinct yet equally crucial roles in ensuring the smooth operation, handling, and safety of a vehicle.
Axle Bearings
Support the substantial weight of the vehicle
Enable smooth rotation of the axle shafts
Maintain proper wheel alignment
Withstand forces generated during acceleration, braking, and cornering
Failure can lead to vibrations, noise, and potential damage to other drivetrain components
Wheel Bearings
Facilitate smooth rotation of the wheels on the axle shafts
Reduce friction and minimize wear on other suspension components
Contribute to vehicle stability and handling, especially during cornering, braking, and acceleration
Prevent uneven tire wear and potential wheel separation, ensuring safety
Signs of Failure
Identifying the signs of a failing axle bearing or wheel bearing is crucial to prevent further damage and ensure safe operation. Early detection can save you from costly repairs and potential safety hazards.
Axle Bearing Failure Symptoms
Noise (grinding, rumbling, or howling) that changes pitch with vehicle speed
Vibrations felt through the vehicle's floor or steering wheel
Leaking differential fluid (in the case of rear axle bearings)
Wheel Bearing Failure Symptoms
Grinding, growling, or humming noise that increases with vehicle speed
Vibrations felt through the steering wheel or seat
Uneven tire wear
ABS warning light illumination (in some cases)
Replacement Costs
The cost of replacing axle bearings or wheel bearings can vary significantly depending on several factors:
Vehicle make and model
Labor rates in your area
Additional components that may need replacement (e.g., hub assembly, ABS sensor)
Axle Bearing Replacement Cost
| Cost Factor | Range |
|---|---|
| Parts (per bearing) | $50 - $200 |
| Labor | $50 - $200 |
| Total Cost (per bearing) | $100 - $400 |
Wheel Bearing Replacement Cost
| Cost Factor | Range |
|---|---|
| Parts (per wheel) | $100 - $300 |
| Labor | $100 - $300 |
| Additional Components (if required) | $50 - $200 |
| Total Cost (per wheel) | $200 - $600 |
It's important to note that replacing wheel bearings is generally more expensive than replacing axle bearings due to the additional components involved, such as the hub assembly and ABS sensor.
Maintenance and Prevention
Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for extending the lifespan of both axle bearings and wheel bearings. Here are some tips to help prevent premature failure:

Follow the manufacturer's recommended service intervals
Have a qualified mechanic inspect these components during routine maintenance
Avoid harsh driving conditions, such as frequently driving over potholes or curbs
Maintain proper lubrication levels
Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage and more costly repairs
By adhering to these preventive measures, you can ensure the longevity of your vehicle's axle bearings and wheel bearings, contributing to a safer and more enjoyable driving experience.
Conclusion
While axle bearings and wheel bearings serve different purposes, they are both critical components that contribute to the smooth operation and safety of a vehicle. Understanding the distinction between these two components, their functions, and the signs of failure can help vehicle owners address issues promptly and make informed decisions regarding maintenance and repairs.
Regular inspections, timely replacements, and proper maintenance are essential to ensure a safe and enjoyable driving experience. By investing in the care and upkeep of these components, you can prevent costly repairs and extend the lifespan of your vehicle.
FAQs
What is the primary distinction between axle bearings and wheel bearings?
Axle bearings are located at the ends of axle shafts and support the vehicle's weight, while wheel bearings are inside the wheel hub assembly and facilitate smooth wheel rotation.
Can axle bearings and wheel bearings be used interchangeably?
No, axle bearings and wheel bearings serve different purposes and are not interchangeable components.
What types of axle bearings are commonly used?
Common types of axle bearings include ball bearings, roller bearings, and tapered roller bearings, each designed for specific load and operating conditions.
How do wheel bearing types differ from axle bearing types?
Wheel bearings primarily use ball bearings and tapered roller bearings, while axle bearings may also include roller bearings and other specialized types.
What happens if an axle bearing fails?
A failed axle bearing can cause vibrations, noise, leaking differential fluid (in rear axles), and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
What are the consequences of a failed wheel bearing?
A failed wheel bearing can lead to grinding or humming noises, vibrations, uneven tire wear, illumination of the ABS warning light, and potential safety hazards.
How often should axle bearings and wheel bearings be inspected?
It is recommended to have a qualified mechanic inspect these components during routine maintenance intervals specified by the manufacturer.
Can driving habits affect the lifespan of axle bearings and wheel bearings?
Yes, harsh driving conditions, such as frequently driving over potholes or curbs, can accelerate the wear and tear on these components.
Is it more expensive to replace axle bearings or wheel bearings?
Generally, replacing wheel bearings is more expensive due to the additional components involved, such as the hub assembly and potential ABS sensor replacement.
What preventive measures can extend the lifespan of axle bearings and wheel bearings?
Proper lubrication, addressing issues promptly, and avoiding harsh driving conditions can help extend the lifespan of these components.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
The 5.3L Vortec engine is a popular V8 engine produced by General Motors (GM) and widely used in various GM trucks and SUVs. It has been a staple in vehicles such as the Chevrolet Silverado, GMC Sierra, Chevrolet Tahoe, and GMC Yukon models, among others.
Your vehicle's suspension system plays a crucial role in providing a smooth and comfortable ride. At the heart of this system lie the coil springs, which are responsible for absorbing road shocks and maintaining proper ride height.
Greetings, fellow automotive aficionados! As a seasoned mechanic, I've encountered countless diagnostic codes, each presenting its own unique challenge. Today, we embark on an odyssey through the intricate realm of the P038C code – "Ignition I Control Signal Circuit High." Buckle up, for we're about to delve into the intricate workings of your vehicle's ignition system, unraveling the mysteries that lie beneath the hood.
Bài viết liên quan
Your vehicle's control arm bushings play a pivotal role in ensuring a smooth and controlled ride. These unassuming rubber or polyurethane components act as cushions between the control arms and the vehicle's frame, absorbing road vibrations and facilitating proper suspension movement.
Struts are an integral part of a vehicle's suspension system, responsible for providing a smooth and comfortable ride while ensuring proper handling and stability. However, like any other component, struts can wear out over time due to various factors.
Maintaining your vehicle's suspension system is crucial for ensuring a smooth and safe ride. One of the most critical components in this system is the ball joint, which allows the wheels to pivot and turn while absorbing the impact of bumps and uneven surfaces.
The Cadillac Escalade is a luxurious full-size SUV known for its impressive performance and advanced features. However, even the most sophisticated vehicles can encounter issues, and one common problem that Escalade owners may face is the dreaded "Service Suspension System" message on the dashboard.
Tie rods are essential components of a vehicle's steering system, playing a critical role in ensuring safe and precise control over the direction of the wheels. These unassuming yet vital parts have been an integral part of automotive engineering for decades, enabling drivers to navigate roads and maneuver their vehicles with confidence.
Axle seals play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of your vehicle's drivetrain system. These unassuming components form a tight seal around the axle shaft, preventing the leakage of lubricating fluid from the axle assembly.
The rack and pinion system is a critical component of a vehicle's steering mechanism, responsible for converting the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear motion, allowing the wheels to turn left or right.
Wheel bearings play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and safe operation of your vehicle's wheels. These components allow the wheels to rotate freely while supporting the entire weight of the car.
The stabilizer bar, also known as the sway bar or anti-roll bar, plays a crucial role in maintaining your vehicle's handling and stability. As a vital component of the suspension system, it helps reduce body roll during turns and ensures optimal tire contact with the road surface.
Your vehicle's suspension system plays a crucial role in providing a smooth and comfortable ride. At the heart of this system lie the coil springs, which are responsible for absorbing road shocks and maintaining proper ride height.












