The P030F code is an OBD-II diagnostic trouble code that indicates a high voltage issue in the Ignition B control signal circuit. This circuit is crucial for the proper functioning of the ignition system, which is responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the engine's cylinders. When this code is triggered, it can lead to engine misfires, poor performance, and increased emissions.
Integrated Starter Generator (ISG): Boosting Efficiency in Hybrid Vehicles
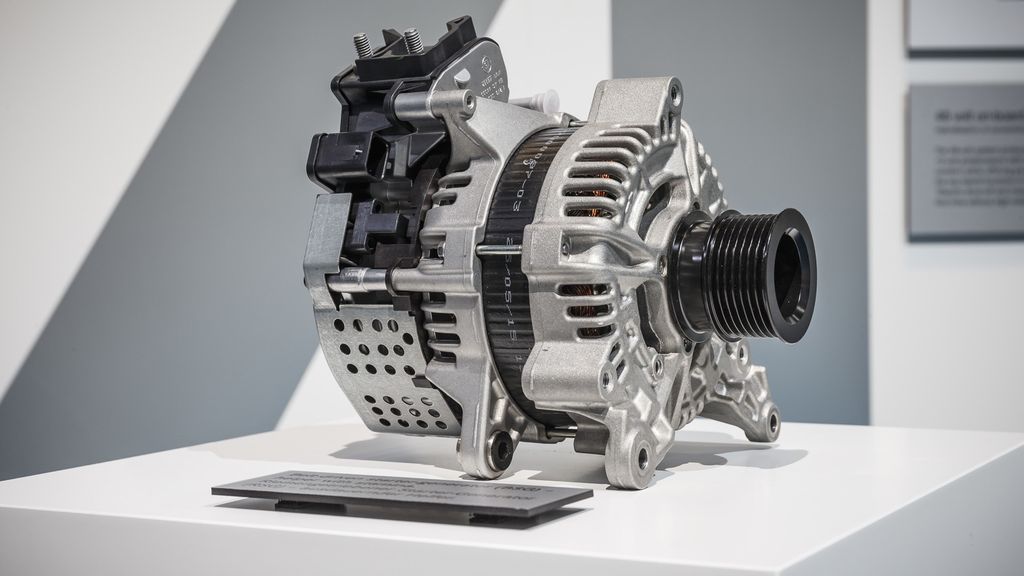
Integrated Starter Generator (ISG): Boosting Efficiency in Hybrid Vehicles
The integrated starter generator (ISG) is a revolutionary innovation in hybrid vehicle technology, seamlessly combining the functions of a traditional starter motor and alternator into a single, efficient unit. This groundbreaking device is transforming the way hybrid vehicles operate, resulting in improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced performance. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of ISGs, their benefits, mechanisms, and the future potential of this technology.
Introduction
Hybrid vehicles have gained immense popularity due to their ability to combine the advantages of internal combustion engines and electric motors. The integrated starter generator plays a crucial role in optimizing the efficiency and performance of these hybrid systems.
This article will delve into the concept of integrated starter generators, their superiority over conventional starters and alternators, and their integral role in the functioning of mild hybrid systems. We will also discuss the adoption trends, major manufacturers, and the future prospects of this technology in the automotive industry.
What is an Integrated Starter Generator?
An integrated starter generator (ISG) is a device that merges the capabilities of a starter motor and an alternator into a single, compact unit. Unlike traditional systems where the starter and alternator work independently, an ISG integrates these essential components, resulting in a more efficient and streamlined power management system.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Mounting | Directly mounted to the engine crankshaft or connected via a belt drive |
| Power Transfer | Efficient power transfer between the ISG and the engine |
| Key Components | High-performance electric motor, power electronics, and control system |
| Configuration | Can be designed for belt-driven or crankshaft-mounted configurations |
The ISG is mounted directly to the engine crankshaft or connected through a belt drive, facilitating efficient power transfer. It performs multiple functions, including cranking the engine during start-up, generating electricity to charge the battery, and providing additional power to assist the engine during acceleration.
Benefits of Integrated Starter Generators
The implementation of integrated starter generators in hybrid vehicles offers numerous benefits that enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and improve the driving experience.
Improved Fuel Efficiency:
ISGs enable start-stop functionality, automatically shutting off the engine when the vehicle stops and restarting it instantly when the accelerator is pressed.
This feature minimizes fuel consumption during idling periods, particularly beneficial in city driving conditions with frequent stops.
Reduced Emissions:
The start-stop capability of ISGs reduces the time the engine spends idling, decreasing the amount of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere.
ISGs facilitate regenerative braking, converting kinetic energy generated during deceleration into electrical energy, which is stored in the battery.
The recovered energy can power the vehicle's electrical systems or provide additional propulsion, further enhancing efficiency and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Enhanced Performance:
ISGs provide additional power to assist the engine during acceleration, improving overall performance and throttle response.
Compact Design:
The integration of starter and alternator functions into a single unit saves space and reduces weight in the vehicle's power management system.
How Integrated Starter Generators Work
At the heart of an integrated starter generator's functionality is its ability to seamlessly combine the roles of a starter motor and an alternator.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Starter | When the vehicle is at rest, the ISG acts as a starter, cranking the engine to initiate the combustion process. |
| Alternator | Once the engine is running, the ISG transitions into its role as an alternator, generating electricity to charge the battery and power the electrical systems. |
The ISG's dual functionality allows for a more efficient power generation and distribution process, optimizing its performance based on the vehicle's specific requirements at any given moment.
Mounting Options:
ISGs can be mounted directly to the engine crankshaft, providing a direct and efficient means of power transfer.
Alternatively, ISGs can be connected via a belt drive system, allowing for more flexible packaging and easier integration with existing engine components.
Power Output and Torque Assist:
ISGs typically offer power outputs ranging from 5 to 20 kW, depending on the specific system and vehicle requirements.
The additional power provided by ISGs can be harnessed to assist the engine during acceleration, resulting in improved throttle response and overall performance.
Role in Mild Hybrid Systems:
ISGs are particularly well-suited for mild hybrid systems, serving as a key component in enhancing efficiency and reducing emissions.
Mild hybrid vehicles leverage the capabilities of ISGs to provide limited electric assist, enabling features such as start-stop functionality and regenerative braking.
While mild hybrids cannot operate solely on electric power like full hybrid or plug-in hybrid vehicles, they offer a cost-effective solution for improving fuel economy and reducing environmental impact.
Adoption and Market Trends
The adoption of integrated starter generators in the automotive industry has been steadily increasing, driven by stringent emissions regulations and growing demand for efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Compared to full hybrid systems, mild hybrid systems equipped with ISGs provide a balance between cost and benefit.
ISGs offer a cost-effective solution for automakers seeking to improve efficiency without significant cost increases.
Major Players:
Leading companies in the ISG market include Bosch, Denso, Continental, and Valeo.
These manufacturers and suppliers offer a range of ISG solutions tailored to different vehicle segments and requirements.
Consumer Demand:
Consumers are increasingly seeking vehicles that offer improved fuel economy and reduced emissions.
ISGs provide a tangible solution to these concerns, making them an attractive feature for environmentally conscious buyers.
Future Developments and Potential
As the automotive industry continues to evolve and embrace electrification, the future of integrated starter generator technology looks promising.
Advancements in Technology:
Ongoing advancements in power electronics and motor design are expected to further enhance the performance and efficiency of ISGs.
These developments will enable even greater fuel savings and emission reductions.
Optimization of Control Strategies:
Future ISGs can leverage advanced algorithms and real-time data analysis to adapt to various driving conditions and optimize performance.
Predictive energy management techniques can anticipate the vehicle's power requirements based on factors such as route, traffic conditions, and driver behavior, allowing for more efficient power distribution and utilization.
Integration with Other Technologies:
ISGs can play a complementary role in more electrified powertrains, working in conjunction with larger electric motors and high-capacity battery systems.
This integration could enable more advanced hybrid architectures, such as plug-in mild hybrids, combining the benefits of ISGs with the ability to charge from an external power source.
Environmental Considerations:
It is crucial to consider the potential environmental impacts associated with the production and disposal of ISGs and their associated components.
Automakers and suppliers must prioritize sustainability and circular economy principles to minimize the environmental footprint of ISGs throughout their lifecycle.
Conclusion
Integrated starter generators have emerged as a transformative technology in the realm of hybrid vehicles, offering a compelling solution for improving efficiency, reducing emissions, and enhancing performance. By combining the functions of a starter motor and an alternator into a single, compact unit, ISGs enable a range of benefits, including start-stop functionality, regenerative braking, and torque assist.
As the automotive industry continues to prioritize sustainability and electrification, the adoption of ISGs is expected to accelerate. With advancements in power electronics, motor design, and control strategies, the potential for further efficiency gains and emission reductions is significant. However, addressing the environmental considerations associated with the production and disposal of ISGs is crucial to ensure a truly sustainable future for transportation.
The integrated starter generator represents a key step in the transition towards more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles. As this technology continues to evolve and mature, it will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping the future of the automotive landscape, contributing to a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable mode of transportation.
FAQs
What is the key difference between an integrated starter generator and a conventional starter motor/alternator system?
An ISG combines the functions of a starter motor and alternator into one unit, while conventional systems have separate components for each role. This integration results in a more efficient and compact power management system.
How does an ISG contribute to improved fuel efficiency in hybrid vehicles?
An ISG enables start-stop functionality, automatically shutting off the engine when stopped to reduce idling and fuel consumption. It also facilitates regenerative braking to recover energy and recharge the battery.
What role does an ISG play in reducing emissions from hybrid vehicles?
By minimizing idling time through start-stop capability and enabling regenerative braking, ISGs help reduce the amount of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere.
Can an ISG provide additional power to assist the engine?
Yes, ISGs can provide supplementary power to assist the engine during acceleration, improving overall performance and throttle response.
What are the typical power output ranges for ISGs?
ISGs typically offer power outputs ranging from 5 to 20 kW, depending on the specific system and vehicle requirements.
How are ISGs mounted in hybrid vehicles?
ISGs can be mounted directly to the engine crankshaft or connected via a belt drive system, allowing for efficient power transfer and flexible packaging.
Which type of hybrid system primarily utilizes ISGs?
ISGs are particularly well-suited for mild hybrid systems, which provide limited electric assist and cannot operate solely on electric power.
What are some major manufacturers and suppliers of ISGs?
Leading companies in the ISG market include Bosch, Denso, Continental, and Valeo, offering a range of ISG solutions for different vehicle segments.
How can future advancements in technology further enhance the performance of ISGs?
Ongoing improvements in power electronics, motor design, and control strategies can enable even greater fuel savings, emission reductions, and performance optimization for ISGs.
What environmental considerations should be addressed regarding ISGs?
The production and disposal of ISGs and their associated components must prioritize sustainability and circular economy principles to minimize their environmental footprint throughout their lifecycle.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
Fuel injectors are a critical component in modern gasoline engines, responsible for delivering the precise amount of fuel required for efficient combustion.
The P0006 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) indicates a low voltage or lack of signal in the fuel shutoff valve "A" control circuit. This issue is detected by the engine control module (ECM) and requires prompt attention to ensure proper fuel system operation and vehicle safety.
The blower motor is a crucial component of an HVAC system, responsible for circulating heated or cooled air throughout a building. When this motor fails, it can lead to inadequate heating or cooling, resulting in discomfort and potential damage to the system.
Bài viết liên quan
In modern automotive electrical systems, the alternator is a critical component that converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy to power various systems and charge the battery. Traditionally, alternators have relied on passive diode rectifiers to convert the alternating current (AC) output of the stator windings into direct current (DC). However, these passive rectifiers have inherent limitations, such as high voltage drop, power losses, and inefficiency, especially at low alternator speeds.
Stop/start alternators are a key component in modern vehicles equipped with stop/start technology, which automatically shuts off the engine when the vehicle comes to a stop and restarts it when the driver releases the brake pedal. These advanced alternators are specifically designed to handle the increased electrical demands and frequent engine restarts associated with stop/start systems, while also contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Wireless charging systems are revolutionizing the way we charge electric vehicles (EVs), offering a convenient, automated, and flexible alternative to conventional plug-in charging. This emerging technology allows EVs to charge their batteries without the need for physical cables or plugs, simplifying the charging process and opening up new possibilities for EV owners and operators.
Regenerative braking, a groundbreaking technology, has revolutionized the automotive industry, particularly in electric and hybrid vehicles. This innovative system captures kinetic energy during braking and converts it into electricity, storing it in the vehicle's battery pack. By harnessing this energy, regenerative braking enhances vehicle efficiency, prolongs driving range, and minimizes wear on conventional brake components.







