Greetings, fellow gearheads! As an automotive mechanic with years of experience under my belt, I've encountered my fair share of diagnostic trouble codes. Today, we're going to delve deep into the enigmatic world of the P0393 code – a code that can leave even the most seasoned mechanics scratching their heads in bewilderment.
Can a Clogged Transmission Filter Cause No Drive? Symptoms & Solutions
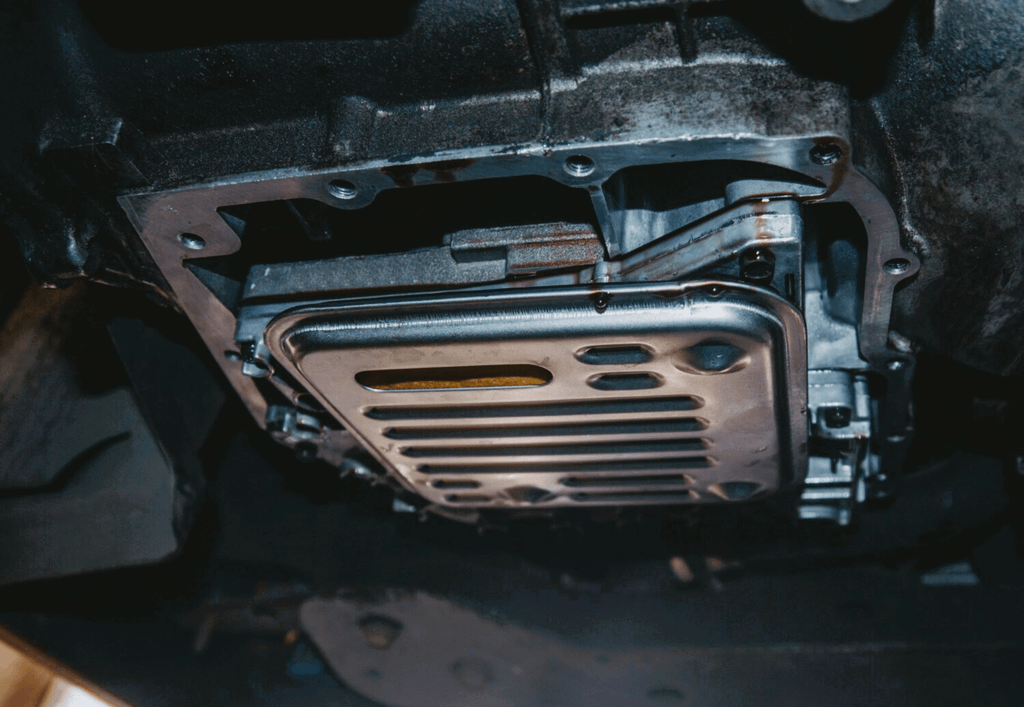
Can a Clogged Transmission Filter Cause No Drive? Symptoms & Solutions
The transmission system is a critical component in your vehicle, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. At the heart of this system lies the transmission filter, a seemingly small component that plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation. In this comprehensive article, we'll explore the potential consequences of a clogged transmission filter, including the dreaded "no drive" condition, and provide you with valuable insights into diagnosis, repair, and preventive maintenance.

I. Understanding the Transmission Filter
Before delving into the potential issues caused by a clogged filter, it's essential to understand the function and importance of this crucial component.
The transmission filter is designed to remove contaminants and debris from the transmission fluid, ensuring that the internal components of the transmission system are properly lubricated and protected from excessive wear and tear. By trapping harmful particles and impurities, the filter helps extend the lifespan of the transmission and prevents premature component failure.
| Filter Function | Importance |
|---|---|
| Removes contaminants and debris | Protects internal components |
| Maintains clean transmission fluid | Ensures proper lubrication |
| Traps harmful particles | Prevents excessive wear |
| Extends transmission lifespan | Avoids premature component failure |
The filtration process is straightforward: as the transmission fluid circulates through the system, it passes through the filter media, which captures and retains contaminants. The filter's design and porosity determine its ability to remove particles of varying sizes, ranging from microscopic debris to larger particles.
Regular maintenance and timely filter replacement are crucial to ensure the transmission system's longevity and optimal performance. Most manufacturers recommend changing the transmission filter and flushing the fluid at specific mileage intervals or time periods, typically ranging from 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle make and model.
II. Signs of a Clogged Transmission Filter
As the transmission filter becomes increasingly clogged, it can manifest in various ways, and it's crucial to recognize the warning signs to address the issue promptly. Here are some common indicators of a clogged transmission filter:
Difficulty Shifting Gears
One of the most noticeable signs of a clogged filter is difficulty shifting gears. The transmission may hesitate, slip, or delay engagement when attempting to shift, resulting in a jerky or rough shifting experience. This can be particularly noticeable when accelerating from a stop or when shifting between gears during highway driving.
Strange Noises
As the filter becomes increasingly clogged, it can cause unusual noises to emanate from the transmission. These may include whining, grinding, or rattling sounds, which can indicate a lack of proper lubrication or excessive wear on internal components such as gears, bearings, and clutches.
| Noise Type | Potential Cause |
|---|---|
| Whining | Lack of lubrication |
| Grinding | Excessive wear on gears |
| Rattling | Worn bearings or clutches |
Transmission Fluid Leaks
A severely clogged filter can create excessive pressure within the transmission system, potentially leading to fluid leaks. If you notice puddles of reddish fluid under your vehicle, it could be a sign of a transmission issue, including a clogged filter.
Burning Smell
Restricted fluid flow due to a clogged filter can cause the transmission to overheat, resulting in a distinct burning smell. This odor is often accompanied by increased transmission temperatures and potential fluid degradation, which can further exacerbate the problem.
Warning Lights and Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Modern vehicles are equipped with warning lights and diagnostic systems that can alert you to transmission issues. If the check engine light or transmission warning light illuminates, it's essential to have the vehicle diagnosed by a professional mechanic, who can retrieve and interpret any diagnostic trouble codes related to the transmission system.
| Warning Sign | Potential Issue |
|---|---|
| Check Engine Light | Transmission problem detected |
| Transmission Warning Light | Transmission issue identified |
| Diagnostic Trouble Codes | Specific transmission fault codes |
III. The Mechanism Behind a "No Drive" Condition
In severe cases, a severely clogged transmission filter can restrict fluid flow to the point where the transmission fails to engage or respond when accelerating, resulting in a "no drive" condition. This scenario can be alarming and potentially dangerous, leaving you stranded on the road.
The mechanism behind this issue is a cascading effect of restricted fluid flow, reduced hydraulic pressure, and impaired component engagement.
Restricted Fluid Flow
When the transmission filter becomes excessively clogged, it impedes the flow of transmission fluid throughout the system. This restricted flow can have cascading effects on various components and functions.
Reduced Hydraulic Pressure
Adequate fluid flow is essential for maintaining proper hydraulic pressure within the transmission system. A clogged filter can significantly reduce this pressure, affecting the engagement of critical components such as clutches and bands.
Impaired Clutch and Band Engagement
Hydraulic pressure is responsible for engaging the clutches and bands within the transmission, which facilitate gear shifts and power transfer. Reduced pressure can lead to incomplete or improper engagement, resulting in slippage or disengagement of these components.
Gear Slippage and Power Transmission Issues
When the clutches and bands fail to engage correctly, it can cause the gears to slip or disengage entirely, preventing the transmission from transferring power effectively to the wheels. This can manifest as a "no drive" condition, where the vehicle fails to move despite pressing the accelerator pedal.
The severity of the "no drive" condition can vary depending on the extent of the filter clogging and the resulting impact on fluid flow and component engagement. In some cases, the vehicle may still move but with significant power loss or erratic behavior, while in extreme cases, it may not move at all.
IV. Consequences of Driving with a Clogged Filter
Continuing to operate your vehicle with a clogged transmission filter can have severe consequences and lead to costly repairs or even complete transmission failure. Here are some potential consequences of driving with a clogged filter:
Lack of Lubrication
A clogged filter restricts the flow of transmission fluid, which serves as a lubricant for the internal components. Without proper lubrication, excessive friction and wear can occur, leading to premature component failure.
| Component | Potential Damage |
|---|---|
| Gears | Excessive wear, tooth damage |
| Bearings | Increased friction, overheating |
| Clutches | Slippage, premature wear |
| Bands | Increased wear, potential breakage |
Increased Wear on Internal Components
The lack of lubrication caused by a clogged filter can accelerate wear on critical components such as gears, bearings, clutches, and bands. This wear can quickly compound, leading to further damage and potential transmission breakdown.
Overheating and Fluid Degradation
Restricted fluid flow can also cause the transmission to overheat, which can degrade the quality of the transmission fluid. As the fluid breaks down, it loses its lubricating and protective properties, exacerbating the wear and tear on internal components.
Potential Transmission Failure
In extreme cases, driving with a severely clogged transmission filter can lead to complete transmission failure. This can necessitate a costly transmission rebuild or replacement, which can be a significant financial burden.
It's important to note that the consequences of driving with a clogged filter can vary depending on the severity of the clogging, the age and condition of the transmission, and the driving conditions. However, ignoring the warning signs and continuing to operate the vehicle can significantly increase the risk of costly repairs or complete transmission failure.
V. Diagnosing a Clogged Transmission Filter

If you suspect a clogged transmission filter, it's essential to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic who can accurately diagnose the issue. Here are some common diagnostic procedures used to identify a clogged transmission filter:
Visual Inspection
The mechanic will typically begin with a visual inspection of the transmission fluid. Discolored or contaminated fluid can be an indication of a clogged filter or other transmission issues.
| Fluid Condition | Potential Issue |
|---|---|
| Dark or opaque | Contamination, debris |
| Burnt smell | Overheating, fluid degradation |
| Metal particles | Internal component wear |
Fluid Analysis
More advanced diagnostic techniques may involve analyzing a sample of the transmission fluid for contaminants, debris, or signs of wear. This can provide valuable insights into the condition of the filter and the overall transmission system.
Fluid analysis can detect:
Metallic particles (indicating component wear)
Sludge or varnish buildup
Degradation of fluid properties
Pressure Tests
Mechanics may also perform pressure tests to measure the hydraulic pressure within the transmission system. Low pressure readings can indicate a clogged filter or other restrictions in the fluid flow.
| Pressure Reading | Potential Issue |
|---|---|
| Low pressure | Clogged filter, fluid flow restriction |
| High pressure | Blockage, internal component issue |
| Fluctuating pressure | Leaks, component malfunction |
Diagnostic Scans
Modern vehicles are equipped with on-board diagnostic systems that can detect and report transmission-related issues. A mechanic can connect a diagnostic scanner to retrieve any trouble codes or data that may point to a clogged filter or other transmission problems.
Common transmission trouble codes:
P0700 - P0799 (Transmission Control System)
P0800 - P0899 (Transmission Sensors/Switches)
P0900 - P0999 (Transmission Components)
VI. Repair and Maintenance Procedures
Once a clogged transmission filter has been diagnosed, the mechanic will recommend the appropriate repair and maintenance procedures to restore the transmission system's proper function.
Filter Replacement
The primary repair step is to replace the clogged transmission filter with a new one. This ensures that the transmission fluid can flow freely and contaminants are effectively removed from the system.
During the filter replacement process, the mechanic will:
Drain the old transmission fluid
Remove the old filter
Install the new filter
Refill the system with fresh transmission fluid
Fluid Flush and Refill
In addition to replacing the filter, the mechanic will typically perform a complete fluid flush to remove any remaining contaminants or debris from the transmission system. Fresh, clean transmission fluid will then be added to the system.
The fluid flush process involves:
Connecting a flushing machine to the transmission
Circulating a cleaning solution through the system
Removing the old, contaminated fluid
Refilling with new, clean transmission fluid
Transmission Rebuild or Replacement
In cases where the clogged filter has caused significant damage to internal components, a more extensive transmission rebuild or replacement may be necessary. The mechanic will assess the extent of the damage and provide recommendations based on the vehicle's condition and repair costs.
| Repair Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Transmission Rebuild | Disassembling, replacing worn parts, reassembling |
| Transmission Replacement | Installing a new or remanufactured transmission |
The decision between a rebuild or replacement will depend on factors such as the age of the transmission, the extent of damage, and the overall cost-effectiveness of each option.
VII. Preventive Maintenance for Transmission Health
To avoid the issues associated with a clogged transmission filter and maintain the overall health of your transmission system, it's essential to follow a proactive preventive maintenance routine.
Regular Filter Changes
Adhering to the manufacturer's recommended schedule for transmission filter changes is crucial. This helps ensure that the filter is replaced before it becomes excessively clogged and prevents potential damage to the transmission system.
Most manufacturers recommend changing the transmission filter:
Every 30,000 to 100,000 miles
Or every 2 to 5 years (whichever comes first)
Fluid Changes at Recommended Intervals
In addition to filter changes, regular transmission fluid changes are also recommended. Fresh fluid helps maintain proper lubrication, removes contaminants, and extends the life of the transmission components.
Typical transmission fluid change intervals:
Automatic transmissions: Every 60,000 to 100,000 miles
Manual transmissions: Every 30,000 to 60,000 miles
Addressing Warning Signs Promptly
If you notice any warning signs, such as difficulty shifting gears, strange noises, or warning lights, it's essential to have your vehicle inspected by a professional mechanic promptly. Addressing issues early can prevent further damage and costly repairs.
| Warning Sign | Potential Issue |
|---|---|
| Gear slippage | Clutch/band engagement problems |
| Whining noises | Lack of lubrication |
| Warning lights | Transmission system fault |
Importance of Professional Service
While some vehicle owners may be tempted to perform transmission maintenance themselves, it's generally recommended to have a qualified mechanic handle these tasks. Professionals have the necessary expertise, tools, and equipment to properly diagnose and service your transmission system.
Benefits of professional service:
Proper diagnosis and repair
Access to specialized tools and equipment
Adherence to manufacturer specifications
Warranty coverage for parts and labor
VIII. Cost Considerations and Repair Options
The cost of repairing or replacing a transmission system can vary significantly depending on several factors. It's essential to understand the potential costs and available options to make an informed decision.
Filter Replacement and Fluid Flush
A simple filter replacement and fluid flush is typically the most cost-effective option. The parts and labor costs for this service can range from a few hundred dollars to around $500, depending on the vehicle make and model.
Transmission Rebuild
If internal components have sustained significant damage, a transmission rebuild may be necessary. This process involves disassembling the transmission, replacing worn or damaged parts, and reassembling it. The cost of a transmission rebuild can range from $1,500 to $4,000 or more, depending on the complexity of the job and the specific components that need to be replaced.
Transmission Replacement
In cases of severe damage or complete transmission failure, a full replacement may be the only viable option. The cost of a new transmission can range from $2,000 to $6,000 or more, depending on the vehicle make, model, and transmission type.
Factors Affecting Repair Costs
Several factors can influence the overall cost of transmission repairs, including:
Vehicle's age and mileage
Availability of parts (OEM vs. aftermarket)
Labor costs in your region
Complexity of the repair
Warranty coverage (if applicable)
It's important to obtain multiple quotes from reputable repair facilities and weigh the costs against the value of your vehicle. In some cases, a transmission replacement may be more cost-effective than a rebuild, especially for older vehicles or those with high mileage.
IX. Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy transmission system is crucial for ensuring your vehicle's longevity and performance. By understanding the signs of a clogged transmission filter, the underlying mechanisms, and the potential consequences, you can take proactive measures to prevent costly repairs and transmission failure.
Regular maintenance, prompt attention to warning signs, and professional service are key to keeping your transmission running smoothly. While the cost of repairs can vary, addressing issues early and following preventive maintenance schedules can save you significant expenses in the long run.
Remember, a clogged transmission filter can indeed lead to a "no drive" condition, but with proper care and attention, you can avoid this dreaded scenario and enjoy a reliable, well-functioning transmission system for years to come.
FAQs
What is the primary function of a transmission filter?
The transmission filter's primary function is to remove contaminants and debris from the transmission fluid, ensuring proper lubrication and protection of the internal components.
Can a clogged filter cause complete transmission failure?
Yes, a severely clogged transmission filter can restrict fluid flow to the point of causing complete transmission failure, leading to costly repairs or replacement.
How often should the transmission filter be replaced?
Most manufacturers recommend replacing the transmission filter every 30,000 to 100,000 miles or every 2 to 5 years, whichever comes first.
Can I replace the transmission filter myself?
While possible for experienced DIYers, it is generally recommended to have a professional mechanic replace the transmission filter to ensure proper installation and avoid potential complications.
What are the consequences of driving with a clogged filter?
Driving with a clogged transmission filter can lead to lack of lubrication, increased wear on internal components, overheating, fluid degradation, and potential transmission failure.
How can I prevent transmission filter clogging?
Regular transmission fluid changes and adhering to the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule are crucial to preventing transmission filter clogging.
Can a clogged filter cause transmission fluid leaks?
Yes, a severely clogged filter can create excessive pressure within the transmission system, potentially leading to fluid leaks from failed seals or gaskets.
What is the cost of replacing a transmission filter?
The cost of replacing a transmission filter can range from a few hundred dollars to over $500, depending on the vehicle make, model, and labor costs.
Can a clogged filter cause shifting issues?
Yes, a clogged transmission filter can restrict fluid flow, leading to delayed or rough shifting, slippage, and other shifting-related problems.
How do mechanics diagnose a clogged transmission filter?
Mechanics typically perform visual inspections, fluid analysis, pressure tests, and diagnostic scans to identify a clogged transmission filter or other transmission-related issues.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
A broken tone ring can cause significant issues in your vehicle's automatic transmission, leading to poor performance, erratic shifting, and potential damage. In this article, we'll explore the common symptoms of a broken tone ring, the causes of tone ring failure, and how to diagnose and fix these problems to keep your transmission running smoothly.
The P0025 diagnostic trouble code indicates an issue with the camshaft timing being excessively retarded on the exhaust/rear bank (Bank 2) of the engine. This code is directly linked to the variable valve timing (VVT) or variable camshaft timing (VCT) system, which plays a vital role in optimizing engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. In this article, we'll explore the symptoms, causes, diagnostic procedures, and repair solutions for the P0025 code, equipping you with the knowledge to address this issue effectively.
The alternator plays a crucial role in a vehicle's electrical system by charging the battery and powering various components. However, issues with the voltage regulator, which controls the alternator's output, can lead to charging problems. In such cases, bypassing the voltage regulator can serve as a temporary solution to diagnose and troubleshoot the issue.
Bài viết liên quan
In the ever-evolving world of automotive maintenance, ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your vehicle's engine is a paramount concern. One crucial component that plays a vital role in this endeavor is the oil filter
In the world of automotive maintenance, choosing the right oil filter is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity. Among the many brands available, STP oil filters have garnered a reputation for their quality and reliability.
Ensuring proper engine lubrication and protection is crucial for maintaining your vehicle's performance and longevity. Oil filters play a vital role in this process by removing contaminants from the engine oil, preventing wear and tear on critical components.
In the realm of automotive maintenance, selecting the right oil filter is a critical decision that can significantly impact your vehicle's engine performance and longevity. Two prominent brands, K&N and Mobil 1, have established themselves as industry leaders, each offering unique advantages and characteristics.
The automotive industry is no stranger to recalls, and Jeep, a renowned brand under Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA), has recently faced significant recalls due to issues with oil cooler components in several of its models.
The air filter is a critical component in a vehicle's engine, responsible for trapping contaminants such as dust, dirt, and debris before they enter the combustion chamber. However, sometimes oil can find its way into the air filter housing or onto the filter itself, which is not a normal occurrence and can indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed.








