The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P03F0 refers to an issue with the "A" Camshaft Profile Actuator "C" Control being stuck on Bank 1. This code is part of the OBD-II system, which monitors the performance of various systems and components in modern vehicles. When the Engine Control Module (ECM) detects a malfunction within the camshaft profile control circuit, it triggers this specific code.
Riveted vs Bonded Brake Shoes: Pros, Cons, and Key Differences Explained
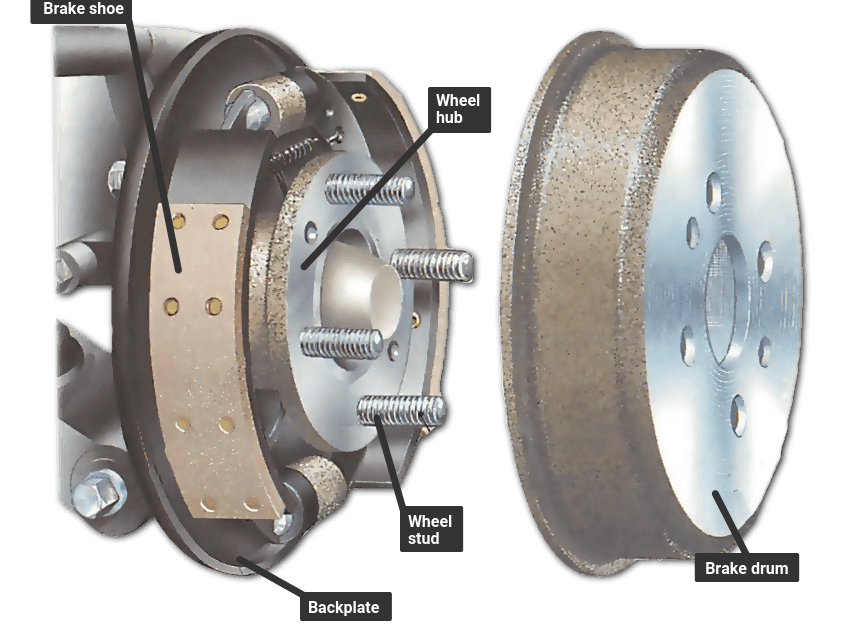
Riveted vs Bonded Brake Shoes: Pros, Cons, and Key Differences Explained
Introduction
Brake shoes are a crucial component of the braking system in vehicles, particularly in drum brake systems. They play a vital role in slowing down and stopping the vehicle by creating friction against the rotating brake drum.

Understanding the Fundamentals
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let's establish a solid foundation by understanding the basics of brake shoes.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Brake Shoes | The components that press against the brake drum to create friction, slowing down or stopping the vehicle's wheels. |
| Riveted Brake Shoes | Feature a woven lining material attached to the shoe using rivets. |
| Bonded Brake Shoes | Have a lining material that is bonded or glued directly to the shoe surface. |
Wear and Tear: An Ongoing Battle
One of the primary concerns when it comes to brake shoes is their susceptibility to wear and tear. Both riveted and bonded linings experience gradual wear due to the constant friction against the brake drum. However, there are distinct differences in how each type handles this wear.
Bonded Linings
Prone to delamination (separation of the lining material from the shoe)
Delamination can lead to reduced braking performance and potential safety hazards
Riveted Linings
Generally more resistant to delamination
Rivets provide a secure mechanical attachment between the lining and the shoe
Over time, rivets can become loose or corroded, causing noise and uneven wear
Heat Dissipation: A Crucial Factor
Braking generates a significant amount of heat, and how well this heat is dissipated can have a profound impact on the longevity and performance of the brake shoes.
Advantages of Riveted Linings:
Rivets act as heat sinks, helping to dissipate heat more effectively
Better heat dissipation leads to improved longevity and performance
Disadvantages of Bonded Linings:
Excessive heat buildup can lead to:
Cracking
Glazing
Complete separation of the lining from the shoe
Contamination: A Silent Threat
Oil or brake fluid leaks can be detrimental to both riveted and bonded brake shoes, as they can contaminate the friction material, leading to reduced braking performance.
However, bonded linings are generally more susceptible to contamination due to their porous nature. The lining material can absorb contaminants, compromising its ability to generate sufficient friction.
Installation Challenges
Proper installation is crucial for both riveted and bonded brake shoes to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Let's explore the installation challenges for each type.
Riveted Linings
Riveting process must be done correctly:
Start from the center and work outwards
Ensure even distribution of pressure
Prevent uneven wear
Chamfering (beveling) the lining edges is essential to prevent noise and uneven wear
Bonded Linings
Meticulous surface preparation is required
Adherence to the adhesive manufacturer's guidelines is crucial
Failure to follow instructions can result in:
Premature delamination
Improper bonding
Reduced braking performance
Potential safety issues
Repair and Replacement Procedures
When it comes to repairing or replacing brake shoes, the processes for riveted and bonded linings differ significantly.
| Riveted Shoes | Bonded Shoes |
|---|---|
| Remove old rivets and lining material using a chisel or drill | Specialized tools and techniques required, such as heat application |
| Clean the shoe surface thoroughly | Meticulous surface preparation according to manufacturer's instructions |
| Install new woven lining material using a rivet tool | Apply new bonded lining material following adhesive guidelines |
| Chamfer (bevel) the lining edges to prevent noise and uneven wear | Chamfer the lining edges to ensure optimal performance |
Cost Considerations
The cost of brake shoe replacement can vary depending on several factors, including:
Parts Cost
Riveted linings: $40 to $100 per axle
Bonded linings: $60 to $120 per axle (depending on quality and vehicle type)
Labor Cost
Professional labor costs: $120 to $200 per axle
DIY: Significantly reduced costs, but requires mechanical skills and proper tools
| Cost Factor | Riveted Linings | Bonded Linings |
|---|---|---|
| Parts Cost | $40 - $100 per axle | $60 - $120 per axle |
| Labor Cost | $120 - $200 per axle (professional) | $120 - $200 per axle (professional) |
| DIY Option | Reduced costs, requires skills and tools | Reduced costs, requires skills and tools |
Preventing Recurring Issues

Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn brake shoes are crucial to preventing recurring issues and ensuring safe braking performance. Here are some key preventive measures:
Adhere to the manufacturer's recommended intervals or replace shoes when they reach the minimum lining thickness
Proper driving habits:
Avoid excessive braking
Avoid riding the brakes
Promptly repair any oil or brake fluid leaks to prevent contamination
Follow the vehicle manufacturer's recommendations for the appropriate lining material (riveted or bonded) for your specific application
Conclusion
In the world of automotive brakes, the choice between riveted and bonded brake shoes is a complex one, with each option offering its own advantages and drawbacks. As a mechanic, I've witnessed firsthand the impact of these choices on braking performance, safety, and overall vehicle maintenance.
While riveted linings generally offer better heat dissipation and resistance to delamination, bonded linings can provide superior braking performance when properly installed and maintained. Ultimately, the decision should be based on a thorough understanding of the vehicle's specific requirements, driving conditions, and the owner's maintenance preferences.
Regardless of the choice, regular inspections, timely replacements, and adherence to proper installation procedures are paramount to ensuring safe and reliable braking performance. By embracing best practices and staying informed, we can navigate the complexities of brake systems with confidence and expertise.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of riveted brake shoes?
Riveted brake shoes offer better heat dissipation and are generally more resistant to delamination or separation of the lining from the shoe. The rivets provide a secure mechanical attachment between the lining and shoe.
What are the key benefits of bonded brake shoes?
Bonded brake shoes can provide superior braking performance when properly installed and maintained. They also allow for a thicker lining material since there are no rivet holes.
Which type lasts longer - riveted or bonded?
There is no definitive answer, as longevity depends on various factors like driving conditions, maintenance, and installation quality. However, riveted shoes are often considered more durable overall.
Are bonded shoes more prone to contamination?
Yes, the porous nature of bonded lining materials makes them more susceptible to absorbing contaminants like oil or brake fluid, which can degrade braking performance.
What happens if brake shoes wear down too much?
Excessively worn brake shoes, whether riveted or bonded, can lead to reduced braking power, noise, vibration, and potential safety hazards like brake fade or lockup.
Can I replace just one brake shoe at a time?
No, brake shoes should always be replaced as a complete axle set (two shoes) to ensure even braking performance on both wheels.
Is special training required to install bonded brake shoes?
Yes, meticulous surface preparation and adherence to the adhesive manufacturer's guidelines are crucial for proper bonded shoe installation and longevity.
Do vehicle manufacturers have preferences?
Some vehicle manufacturers may recommend or prefer one type over the other based on their specific brake system designs and performance requirements.
Can I convert from riveted to bonded shoes or vice versa?
While possible, converting brake shoe types is generally not recommended as it may require modifications to the brake components and could impact braking performance.
How often should brake shoes be inspected?
Brake shoes should be inspected regularly, typically every 12,000 miles or annually, and replaced when they reach the minimum lining thickness specified by the manufacturer.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
Service brake assist is a safety feature found on many modern vehicles that helps reduce stopping distance during emergency braking situations. When the brake pedal is pressed very quickly, the brake assist system automatically increases brake pressure to maximum, helping slow the vehicle down faster than the driver could alone.
The open loop fault is a frustrating issue that can significantly impact your vehicle's performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. When the engine control unit (ECU) detects a problem with one or more sensors, it enters open loop mode, relying on pre-programmed values instead of real-time data. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the causes, effects, and provide step-by-step instructions to diagnose and repair this vexing issue, restoring your vehicle to optimal operating condition.
Brake lines are an integral part of a vehicle's braking system, responsible for transmitting hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder to the wheel cylinders or calipers. This pressure application enables the brakes to slow down or stop the vehicle effectively. Understanding brake lines' functionality, components, maintenance requirements, and replacement procedures is crucial for ensuring optimal braking performance and vehicle safety.




