The rear differential is a crucial component of your vehicle's drivetrain system, responsible for transferring power from the transmission to the rear wheels. It allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, ensuring smooth and efficient power delivery.
Torque Converter Noise at Idle: Diagnosing and Fixing Rattling Sounds
Torque Converter Noise at Idle: Diagnosing and Fixing Rattling Sounds
Introduction
A torque converter is a crucial component in an automatic transmission system, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the transmission. It acts as a fluid coupling, allowing the engine to spin independently from the transmission when the vehicle is stationary or at low speeds. At idle, when the engine is running but the vehicle is not moving, the torque converter can sometimes produce noises that may indicate potential issues.

The Torque Converter: A Brief Overview
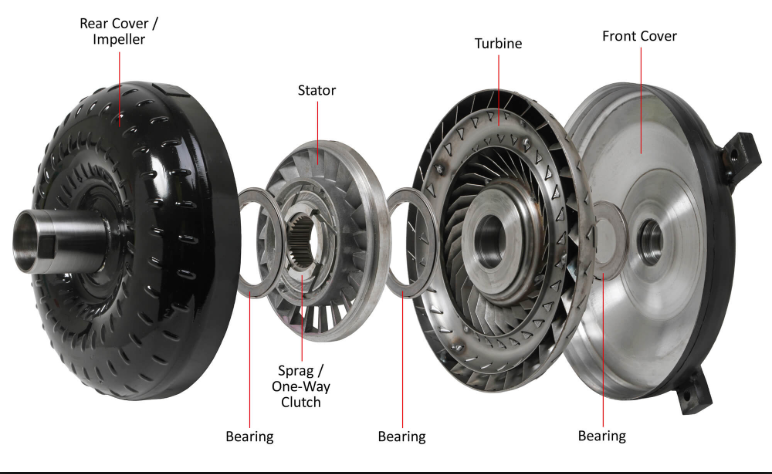
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of torque converter noise, let's take a moment to understand what this little guy does. The torque converter is a crucial component of an automatic transmission, acting as a fluid coupling between the engine and the transmission. Its primary function is to transfer power from the engine to the transmission while allowing for a smooth transition between different gear ratios.
Here's a quick breakdown of the torque converter's main components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Impeller | Driven by the engine, it circulates transmission fluid. |
| Turbine | Receives fluid from the impeller and turns the transmission input shaft. |
| Stator | Redirects fluid flow to increase torque multiplication. |
| Housing | Encloses the components and contains the transmission fluid. |
The Culprits Behind the Noise
Now, let's get to the heart of the matter – the main causes of torque converter noise at idle. Believe me, I've seen them all, and each one has its own unique story to tell.
Worn or Damaged Torque Converter Bearings
The torque converter contains tiny needle bearings that allow the impeller, turbine, and stator to spin smoothly. Over time, these bearings can wear out, causing a whining or rattling noise at idle when the torque converter is stalling. It's like a tiny orchestra of metal-on-metal, and trust me, it's not a pleasant symphony.
Here are some common signs of worn torque converter bearings:
Whining or rattling noise that increases with engine RPM
Noise that changes pitch or volume as the transmission shifts gears
Vibrations felt through the gear selector or floorboard
Broken or Loose Torque Converter Fins/Vanes
Inside the torque converter, there are fins or vanes on the impeller and turbine that circulate transmission fluid. If these fins break off or become loose, they can rattle around inside the converter housing, creating a noise that will make you want to pull your hair out.
Symptoms of broken or loose fins/vanes include:
Rattling or grinding noise, especially at idle or low speeds
Noise that changes with engine RPM or transmission engagement
Possible transmission fluid contamination or leaks
Cracked or Damaged Torque Converter Housing
A cracked or damaged torque converter housing can be a real nightmare. It can allow debris to enter and damage the internal components, leading to rattling noises that will have you questioning your sanity.
Signs of a cracked or damaged housing may include:
Rattling or grinding noise, often constant and not affected by engine RPM
Transmission fluid leaks or contamination
Visible cracks or damage to the housing exterior
Loose Torque Converter Bolts
If the bolts securing the torque converter to the flexplate or crankshaft come loose, it can cause a rattling noise as the converter shifts position. It's like having a loose screw in your head – literally.
Symptoms of loose torque converter bolts:
Rattling noise, especially during acceleration or deceleration
Noise that changes with engine load or transmission engagement
Possible transmission fluid leaks or contamination
Low or Contaminated Transmission Fluid
Dirty or burnt transmission fluid can cause the torque converter to operate less efficiently, leading to increased noise and vibration. It's like trying to run a marathon with a pair of worn-out sneakers – it's just not going to work well.
Signs of low or contaminated transmission fluid:
Whining or grinding noise, often more pronounced at higher RPMs
Slipping or harsh shifting of gears
Transmission fluid discoloration or burnt smell
Diagnosing the Problem
Now, you might be thinking, "Okay, mechanic, how do I figure out what's causing this infernal noise?" Well, my friends, let me walk you through the diagnostic process.
First, we'll check the transmission fluid level and condition. Low or discolored fluid can be a telltale sign of internal issues. Next, we'll break out the mechanic's stethoscope and listen for noises near the bell housing area. Noises that change with engine RPM often indicate a torque converter issue.
We'll also perform a stall speed test by putting the transmission in drive, applying the brakes, and flooring the accelerator for 2-3 seconds. Low stall speeds can be a clear indicator of torque converter problems.
Additionally, we'll check for diagnostic trouble codes related to the torque converter clutch or solenoid using a scan tool. And let's not forget to inspect the flexplate for cracks, which can also cause rattling noises.
Here's a handy table summarizing the diagnostic steps:
| Diagnostic Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Check transmission fluid level and condition | Identify low fluid or contamination |
| Listen with a stethoscope | Pinpoint noise location and characteristics |
| Perform a stall speed test | Check for low stall speeds indicating torque converter issues |
| Scan for diagnostic trouble codes | Identify any torque converter-related codes |
| Inspect the flexplate | Check for cracks that could cause rattling |
Fixing the Problem
Alright, so we've identified the culprit. Now, it's time to roll up our sleeves and get to work.

Worn Bearings/Broken Fins
If the issue is worn bearings or broken fins, the solution is straightforward – replace the entire torque converter assembly. It's like getting a brand-new heart for your transmission.
Cracked Housing
If the housing is cracked, we'll need to replace the torque converter. It's not worth risking further damage by trying to patch it up.
Loose Bolts
For loose bolts, we'll tighten them to the specified torque and use thread locker. We'll also inspect for any damage and replace components if necessary.
Contaminated Fluid
If the transmission fluid is contaminated, we'll drain and refill with new fluid and a fresh filter. If needed, we'll also flush the cooler lines to ensure everything is squeaky clean.
Throughout the repair process, we'll follow the proper procedures for removing and reinstalling the torque converter, using the correct tools and torque specifications. Trust me; you don't want to mess around with this stuff.
Here's a quick overview of the repair steps:
| Repair Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Replace torque converter assembly | For worn bearings or broken fins |
| Replace torque converter | For cracked or damaged housing |
| Tighten bolts and inspect for damage | For loose bolts |
| Drain and refill transmission fluid | For contaminated fluid |
| Flush cooler lines | If needed, to remove contaminants |
Prevention is Key
As with most automotive issues, prevention is key when it comes to torque converter noise. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
Change your transmission fluid and filter at the recommended intervals, using the correct fluid type for your vehicle.
Avoid aggressive driving that can overheat or overload the torque converter.
Check for any leaks that could allow fluid contamination.
Properly tighten the torque converter bolts during installation.
Address any transmission issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Here's a handy checklist for preventive maintenance:
[ ] Change transmission fluid and filter regularly
[ ] Avoid aggressive driving habits
[ ] Inspect for fluid leaks
[ ] Properly tighten torque converter bolts
[ ] Address transmission issues promptly
The Cost of Silence
Now, let's talk about the elephant in the room – the cost of fixing a torque converter noise issue. The cost to replace a torque converter can range from $150 to $500 or more for the part alone, depending on your vehicle. Labor costs for removal and installation can add several hundred dollars to the total.
While it might seem like a hefty price tag, addressing the issue promptly can prevent more expensive transmission repairs down the line. Trust me; you don't want to ignore this problem and end up with a transmission rebuild on your hands.
Here's a rough estimate of the potential costs:
| Repair | Part Cost | Labor Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Torque converter replacement | $150 - $500+ | $300 - $600 |
| Transmission fluid change | $50 - $150 | $50 - $150 |
| Transmission rebuild | $1,500 - $4,000+ | $500 - $1,000+ |
Conclusion
Torque converter noise at idle can be a real headache, but with the right knowledge and a little elbow grease, it's a problem that can be tackled head-on. Remember, prevention is key, and addressing issues promptly can save you a lot of hassle and money in the long run.
So, the next time you hear that whining or rattling sound coming from your transmission, don't panic. Just give your friendly neighborhood mechanic a call, and we'll get to the bottom of it together. After all, that's what we're here for – to keep your ride running smoothly and your sanity intact.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a torque converter?
A torque converter transfers engine power to the transmission and provides torque multiplication for smooth acceleration from a stop. It acts as a fluid coupling between the engine and transmission in an automatic transmission vehicle.
What causes torque converter noise at idle?
Worn or damaged torque converter bearings, broken or loose fins/vanes, cracked or damaged housing, loose torque converter bolts, and low or contaminated transmission fluid can all cause noises from the torque converter area when idling.
How can I diagnose the source of torque converter noise?
Check transmission fluid level and condition first. Then perform a stall speed test, listen with a mechanic's stethoscope near the bell housing area, and scan for diagnostic trouble codes related to the torque converter.
Can I drive with a noisy torque converter?
No, it is not recommended to continue driving with a noisy torque converter as it can lead to further damage and potential transmission failure.
How is a faulty torque converter repaired?
In most cases, the entire torque converter assembly needs to be replaced if it is the source of noise or other issues. Attempting to repair individual components is uncommon.
Can a bad torque converter damage the transmission?
Yes, a faulty torque converter can cause the transmission to overheat and sustain internal damage. Debris from the converter can also circulate and damage other transmission components.
How much does it cost to replace a torque converter?
The cost for just the torque converter part can range from $150 to over $500 depending on the vehicle. Labor costs for removal and installation add several hundred dollars more.
How often should I change transmission fluid?
Follow the manufacturer's recommended intervals for transmission fluid and filter changes, typically every 30,000 to 100,000 miles depending on driving conditions and fluid type.
What are signs of low transmission fluid?
Signs of low transmission fluid include difficulty shifting gears, slipping between gears, overheating transmission, and whining or grinding noises from the transmission area.
Can I prevent torque converter issues?
Yes, changing transmission fluid regularly, avoiding aggressive driving, fixing any leaks promptly, and addressing transmission issues early can help prevent torque converter problems.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
As an automotive mechanic with years of experience, I've encountered a myriad of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). One that often puzzles many is the P035F code, which refers to an issue with the ignition coil "F" control signal circuit. This code is manufacturer-specific, meaning its exact definition can vary slightly depending on the vehicle make. However, the underlying principles remain consistent. In this article, I'll walk you through the main causes, diagnostic steps, repair instructions, and preventive measures for the P035F code.
Driving with bad brake rotors is not advisable or safe, as it can significantly compromise your vehicle's braking performance and increase the risk of accidents. While it may be tempting to put off repairs for convenience or financial reasons, the dangers associated with worn or damaged rotors far outweigh any short-term benefits. In this article, we will explore the signs of bad brake rotors, the safety risks involved, and the importance of regular maintenance to ensure optimal braking performance.
The P0314 code is an OBD-II trouble code that indicates a single cylinder misfire without specifying which cylinder is affected. This code is part of a broader category of misfire codes (P0300-P0319) that can be triggered by various issues related to the ignition, fuel, or mechanical systems of the engine.
Bài viết liên quan
The "Transmission Fault Service Now" warning message is a common issue faced by many Ford vehicle owners, particularly those with automatic transmissions. This warning light indicates that the vehicle's transmission control module (TCM) has detected a fault or problem within the transmission system.
Having issues with your car not going into park or not starting can be frustrating and concerning. These problems can arise due to various reasons, ranging from minor issues to more significant underlying problems with the vehicle's systems.
Manual transmissions, also known as stick shifts or standard transmissions, use a clutch and a system of gears to transfer power from the engine to the wheels. This mechanism allows the driver to control the amount of power delivered to the wheels and adjust the gear ratios based on driving conditions.
An automatic transmission is designed to provide smooth and seamless gear shifts as the vehicle accelerates or decelerates. However, a common issue that many drivers experience is a jerking or shuddering sensation when the transmission shifts from 1st to 2nd gear.
P0700 is a generic OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) trouble code that indicates a malfunction in the transmission control system of a vehicle. This code is triggered when the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or Engine Control Module (ECM) detects an issue with the Transmission Control Module (TCM) or the components it manages.








