The exhaust system is a crucial component of a vehicle, responsible for expelling harmful gases produced during the combustion process. It plays a vital role in reducing noise levels, improving fuel efficiency, and minimizing environmental impact.
Transmission Fault Service Now Error: Causes and Solutions for Ford Vehicles
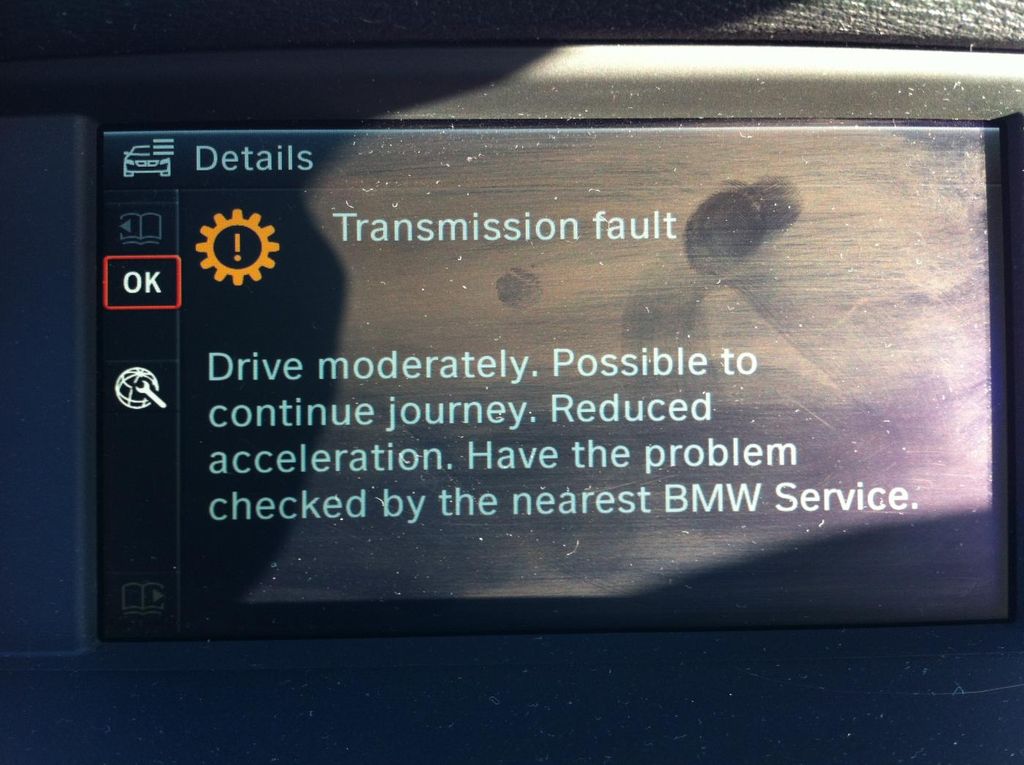
Transmission Fault Service Now Error: Causes and Solutions for Ford Vehicles
Introduction
The "Transmission Fault Service Now" warning message is a common issue faced by many Ford vehicle owners, particularly those with automatic transmissions. This warning light indicates that the vehicle's transmission control module (TCM) has detected a fault or problem within the transmission system. The transmission is a critical component responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to accelerate, maintain speed, and change gears smoothly. When this warning appears, it signifies that the transmission is not functioning correctly, which can lead to various drivability issues and potential safety concerns if left unaddressed.

Common Causes of Transmission Faults
Transmission faults can arise from various issues, and understanding the root causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and repair. Here are some of the most common culprits:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Low Transmission Fluid Level | Leaks or lack of maintenance can lead to a low fluid level, causing excessive wear, overheating, and potential transmission failure. |
| Contaminated or Burnt Transmission Fluid | Over time, the fluid can break down and become contaminated with debris, leading to sluggish shifts, slippage, and transmission failure. |
| Faulty Sensors and Components | Malfunctioning speed sensors, solenoids, or the transmission control module (TCM) can provide inaccurate data, resulting in erratic shifting or loss of gear control. |
| Internal Mechanical Issues | Worn clutches, bands, or gears can cause significant transmission problems due to the immense stress and wear they endure over time. |
Diagnostic Steps for Transmission Faults
When a customer brings in their vehicle with transmission issues, a thorough diagnostic process is essential to identify the root cause. Here are the steps I typically follow:
Fluid Inspection: Check the transmission fluid level and condition (color, smell) to detect any signs of contamination or overheating.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Connect a diagnostic scanner to the vehicle's computer system and scan for any DTCs related to the transmission. These codes provide valuable insights into the specific components or systems that may be causing the issue.
Road Test: Conduct a road test to observe any drivability issues, such as slipping, harsh shifts, or delayed engagements. Pay close attention to the transmission's behavior under various driving conditions.
Component Testing: Based on the DTCs and road test observations, conduct specific tests to diagnose the root cause. This may involve checking the functionality of sensors, solenoids, or other components related to the identified DTCs.
Repair Procedures for Transmission Faults
Once the root cause of the transmission fault has been identified, the appropriate repair procedure can be determined. Here are some common repair scenarios:
Fluid-Related Issues
If the issue is related to low or contaminated transmission fluid, the repair procedure typically involves:
Draining the old fluid
Flushing the system to remove any debris or contaminants
Refilling with fresh, high-quality transmission fluid
Faulty Sensors, Solenoids, or TCM
In cases where faulty sensors, solenoids, or the TCM are identified as the culprit, these components will need to be replaced. It's essential to use genuine or high-quality replacement parts to ensure proper functionality.
Internal Mechanical Repairs
If the issue stems from internal mechanical problems, such as worn clutches, bands, or gears, the repair process becomes more complex and labor-intensive. In these cases, the transmission may need to be disassembled by a specialist, and the faulty components will need to be replaced or rebuilt.
| Repair Type | Description | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Change and Flush | Draining old fluid, flushing the system, and refilling with new fluid. | $100 - $300 |
| Sensor/Solenoid Replacement | Replacing faulty sensors, solenoids, or the TCM. | $300 - $800 |
| Internal Transmission Repairs | Disassembling the transmission, replacing worn components like clutches, bands, or gears. Requires a specialist. | $1,500 - $4,000+ |
Prevention and Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is key to avoiding costly transmission repairs. Here are some essential tips:
Regular transmission fluid and filter changes as recommended by the manufacturer
Avoid aggressive driving habits, such as:
Excessive towing above the rated capacity
Frequent hard acceleration and braking
Get any transmission issues diagnosed and repaired promptly to prevent further damage
Cost Considerations

The cost of repairing a transmission fault can vary significantly depending on the root cause and the extent of the damage. While a simple fluid change and flush may cost between $100 and $300, replacing faulty sensors or solenoids can range from $300 to $800.
However, if the transmission requires internal mechanical repairs, such as a rebuild or overhaul, the costs can escalate rapidly. Depending on the vehicle and the severity of the damage, these repairs can range from $1,500 to $4,000 or even more.
Conclusion
Transmission faults can be a frustrating and potentially costly issue for vehicle owners. However, by understanding the common causes, diagnostic steps, repair procedures, and preventive measures, you can take proactive steps to maintain the health of your transmission and avoid costly repairs.
As an automotive mechanic, I've witnessed firsthand the importance of regular maintenance and prompt attention to transmission issues. By following the recommendations outlined in this article and seeking the expertise of a qualified mechanic, you can ensure your vehicle's transmission remains in top condition, providing you with a smooth and reliable driving experience for years to come.
FAQs
What are the signs of a transmission fault?
Common signs include slipping gears, delayed engagement, strange noises like grinding or whining, and the "Service Transmission" warning light illuminated. Address these issues promptly to prevent further damage.
How do you diagnose a transmission fault?
Check the transmission fluid level and condition, scan for diagnostic trouble codes, conduct a road test to observe drivability issues, and perform specific component tests based on the codes and observations.
What causes low transmission fluid levels?
Low fluid levels are typically caused by leaks or lack of proper maintenance and fluid changes as recommended by the manufacturer.
Why is contaminated transmission fluid problematic?
Contaminated or burnt fluid can break down and become unable to properly lubricate the transmission components, leading to excessive wear, sluggish shifts, slippage, and potential failure.
What role do sensors and components play in transmission faults?
Faulty sensors, solenoids, or the transmission control module (TCM) can provide inaccurate data to the transmission, resulting in erratic shifting or loss of gear control.
What are some common internal mechanical issues in transmissions?
Worn clutches, bands, or gears can cause significant transmission problems due to the immense stress and wear they endure over time.
How can you prevent transmission faults?
Regular transmission fluid and filter changes, avoiding aggressive driving habits like excessive towing or hard acceleration/braking, and promptly addressing any transmission issues can help prevent faults.
What is the typical cost range for a transmission fluid change and flush?
A transmission fluid change and flush typically costs between $100 and $300.
What is the cost range for replacing faulty sensors or solenoids?
Replacing faulty sensors, solenoids, or the TCM can range from $300 to $800, depending on the specific components and labor costs.
What is the potential cost range for internal transmission repairs?
If the transmission requires internal mechanical repairs, such as a rebuild or overhaul, the costs can range from $1,500 to $4,000 or even more, depending on the vehicle and the severity of the damage.
Bình luận (0)
Bài viết đề xuất
If you notice coolant coming out of your vehicle's exhaust, it's a clear sign of a serious issue that requires immediate attention. Coolant leaking into the exhaust system can lead to severe engine damage if left unaddressed. In this article, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and solutions for coolant coming out of the exhaust, helping you understand the importance of prompt action to protect your vehicle's engine.
The diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P03A1 indicates a problem with the cylinder 2 pressure sensor circuit on the vehicle. This sensor is responsible for monitoring the combustion pressure inside cylinder 2 of the engine. The "low" part of the code means the sensor circuit is detecting a voltage lower than expected.
The diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P03B9 indicates that the engine control module (ECM) has detected abnormally high pressure in cylinder 4 of the engine. This code is a generic powertrain code that applies to various vehicle makes and models.
Bài viết liên quan
A torque converter is a crucial component in an automatic transmission system, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the transmission. It acts as a fluid coupling, allowing the engine to spin independently from the transmission when the vehicle is stationary or at low speeds.
Having issues with your car not going into park or not starting can be frustrating and concerning. These problems can arise due to various reasons, ranging from minor issues to more significant underlying problems with the vehicle's systems.
Manual transmissions, also known as stick shifts or standard transmissions, use a clutch and a system of gears to transfer power from the engine to the wheels. This mechanism allows the driver to control the amount of power delivered to the wheels and adjust the gear ratios based on driving conditions.
An automatic transmission is designed to provide smooth and seamless gear shifts as the vehicle accelerates or decelerates. However, a common issue that many drivers experience is a jerking or shuddering sensation when the transmission shifts from 1st to 2nd gear.
P0700 is a generic OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) trouble code that indicates a malfunction in the transmission control system of a vehicle. This code is triggered when the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or Engine Control Module (ECM) detects an issue with the Transmission Control Module (TCM) or the components it manages.









